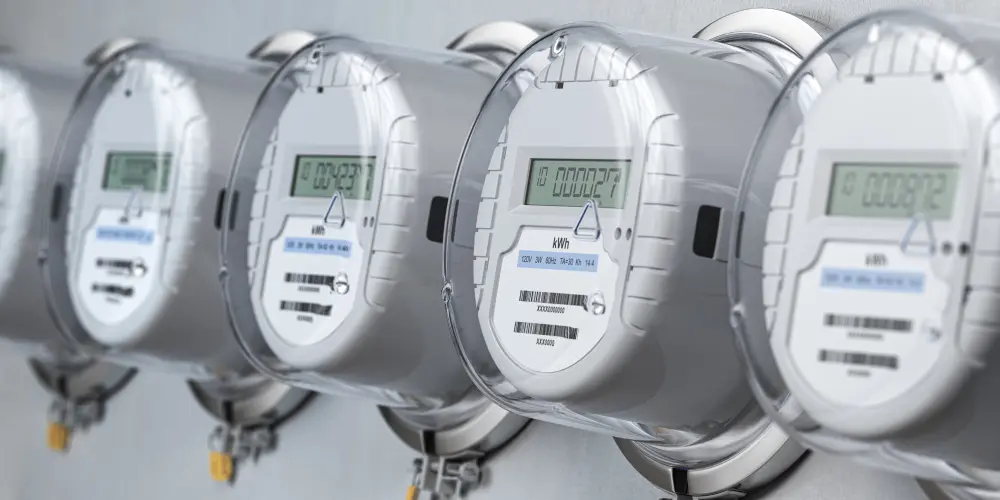
Плюси і мінуси електричних шин
Зміст
ПеремикачЕлектричні шини є ефективними та відомими як компактні рішення для передачі електроенергії в системах розподілу електроенергії.
Вони замінюють традиційні методи електропроводки, підвищуючи надійність і організацію системи.
Однак, як і будь-який електричний компонент, шини мають як переваги, так і обмеження, які необхідно враховувати перед установкою.
Ця стаття досліджує те, що вам потрібно знати про переваги та недоліки електричних шин. Читайте далі, щоб дізнатися більше.
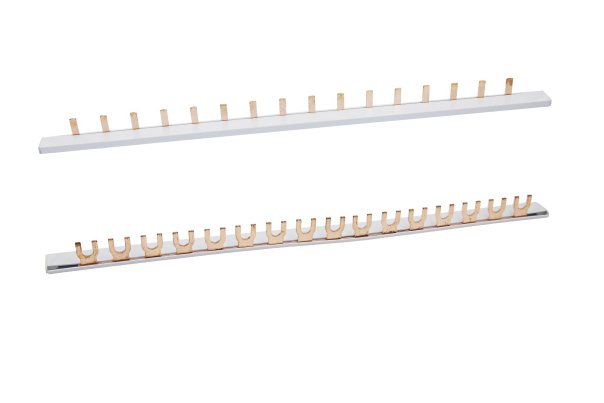
Що таке електрична шина?
Електрична шина — це металева смуга або стрижень, яка проводить електрику в системі розподілу електроенергії.
Зазвичай виготовляється з мідь або алюміній, шини служать централізованими вузлами для передачі електроенергії, що дозволяє ефективно розгалужуватися кількома ланцюгами.
Вони зазвичай використовуються в розподільних пристроях, підстанціях і розподільних щитах для оптимізації електричного підключення та зменшення складності проводки.
Як працює система збірних шин?
Система збірних шин складається з провідників, які розподіляють електроенергію між вхідними та вихідними фідерами.
Він діє як загальна точка підключення, де електричні струми можуть направлятися від джерел живлення до різних ланцюгів.
Система розроблена для безпечної та ефективної обробки навантажень високої напруги, часто включає ізоляцію та захисні кожухи для запобігання електричним збоям.
Плюси електричних шин
1. Ефективність простору та компактний дизайн
На відміну від традиційних кабелів, шини займають значно менше місця.
Їх компактна конструкція дозволяє легше встановлювати в електричні панелі високої щільності, що робить їх ідеальними для застосувань, де простір обмежений.
2. Підвищена електрична ефективність
Шинопроводи мінімізують опір і втрати потужності, підвищуючи загальну електричну ефективність.
Вони дозволяють краще розсіювати тепло, зменшуючи витрати енергії та ризик перегріву порівняно зі звичайною проводкою.
3. Висока міцність і довговічність
Виготовлені з міцних матеріалів, таких як мідь і алюміній, шини можуть витримувати суворі умови навколишнього середовища.
Вони стійкі до корозії та менш схильні до зношування, ніж традиційні кабелі, що забезпечує довший термін служби.
4. Покращена безпека та зниження небезпеки пожежі
Система збірних шин знижує ризик ослаблення з’єднань і перегріву, які є поширеними проблемами в традиційних установках проводки.
Оскільки шини часто укладені в ізольовані кожухи, вони забезпечують кращий захист від електричних несправностей, зменшуючи ймовірність короткого замикання та пожежі.
5. Спрощене встановлення та обслуговування
Шини спрощують розподіл електроенергії, зменшуючи потребу в кількох кабелях і роз’ємах.
Це спрощує установку, усунення несправностей і технічне обслуговування, оскільки інженери можуть легко отримати доступ і змінити з’єднання, не маючи справи з заплутаними проводами.
6. Масштабованість і налаштування
Шинопроводи пропонують гнучкість для майбутнього розширення.
Додаткові схеми можна інтегрувати в систему, не вимагаючи значних модифікацій, що робить їх ідеальними для промислових і комерційних застосувань, які з часом можуть потребувати оновлення.
Мінуси електричних шин
1. Вища початкова вартість
Порівняно з традиційною проводкою шинні системи мають вищу початкову вартість через сучасні матеріали та вимоги до встановлення.
Однак їх довгострокова вигода часто переважує початкові інвестиції.
2. Обмежена гнучкість дизайну
Після встановлення модифікувати шинну систему може бути складно, особливо в обмеженому просторі.
На відміну від гнучких кабелів, шини мають жорстку конструкцію, яка потребує ретельного планування з урахуванням майбутніх змін.
3. Потенційний перегрів в умовах високого навантаження
Незважаючи на те, що шини покращують розсіювання тепла, вони все ще можуть зазнавати теплової напруги під екстремальним навантаженням.
Для підтримки безпечних умов роботи може знадобитися належна вентиляція та механізми охолодження, наприклад повітряне або рідинне охолодження.
4. Сприйнятливість до факторів зовнішнього середовища
Зовнішнє або промислове встановлення вимагає додаткового захисту, щоб запобігти пошкодженню від вологи, пилу та корозійних елементів.
Для високовольтної шини може знадобитися додаткова ізоляція або захисне покриття, щоб підтримувати роботу в суворих умовах.
5. Ризик електричних несправностей у погано спроектованих системах
Якщо шини встановлені неправильно, вони можуть спричинити короткі замикання або дугові змики, що призведе до збоїв системи.
Забезпечення правильної відстані, ізоляції та точок з’єднання має важливе значення для безпечної роботи.
Алюмінієві та мідні збірні шини: з чого виготовлені збірні шини та що краще?
Шинопроводи зазвичай виготовляються з алюміній або мідь, кожна з яких пропонує унікальні переваги:
- Мідні шини забезпечують більш високу провідність, довговічність і стійкість до корозії, що робить їх ідеальними для критичних додатків електроенергії.
- Шинопроводи алюмінієві вони легші та економічніші, але мають нижчу провідність, ніж мідь, тому потрібні більші розміри для роботи з тією самою потужністю струму.
Вибір відповідного матеріалу залежить від застосування, бюджету та умов навколишнього середовища.
Для чого використовується збірна шина?
Шинопроводи використовуються в різних промислових, комерційних і житлових приміщеннях, зокрема:
- Панелі розподілу електроенергії – Використовується на електричних підстанціях і промислових підприємствах для управління потоком електроенергії.
- Розподільні пристрої та панелі керування – Необхідний для високовольтних систем на електростанціях і в центрах обробки даних.
- Системи відновлюваної енергії – Є невід’ємною частиною сонячних електростанцій і вітрових електростанцій, забезпечуючи ефективний розподіл енергії.
- Автомобільні та залізничні системи – Знайдено в електромобілях (EV) і поїздах для полегшення передачі енергії.
Інновації в шинній системі
Завдяки прогресу в технології інтелектуальних мереж шини розвиваються, щоб включати:
- Інтегровані системи моніторингу, які надають дані в реальному часі про умови навантаження та продуктивність.
- Гібридні збірні шини поєднують мідь і алюміній для підвищення ефективності та економічності.
- Удосконалені ізоляційні матеріали, що підвищують довговічність у екстремальних умовах.
Поширені запитання про електричні шини
Як вибирається розмір шини?
Розмір збірної шини визначається на основі вимог системи до пропускної здатності по струму. Такі фактори, як електричне навантаження, теплове розширення та механічна міцність, враховуються для забезпечення безпечного та ефективного розподілу електроенергії.
Які фактори слід враховувати при проектуванні шин?
Основні міркування при проектуванні збірних шин включають форму шин, конфігурацію зовнішніх підстанцій, номінальний показник, теплове розширення, методи з’єднання, підвищення температури, навантаження на ізолятори на вигин, відстань між опорними ізоляторами та зазори між фазами та землею.
Які загальні застосування шин?
Шинопроводи зазвичай використовуються в розподільних пристроях електроживлення, розподільних панелях, підстанціях, промисловому обладнанні, акумуляторних блоках і центрах обробки даних. Їх переваги в конструкції перед традиційною проводкою роблять їх придатними для різних застосувань, що вимагають ефективного розподілу електроенергії.
Плюси та мінуси електричних шин: останні думки
Електричні шини забезпечують ефективне, надійне та масштабоване рішення для розподілу електроенергії в різних галузях промисловості.
Хоча вони мають вищу початкову вартість, їх довгострокові переваги щодо ефективності, безпеки та простоти обслуговування роблять їх цінною інвестицією.
Вибір правильної шинної системи, матеріалу та конструкції має вирішальне значення для оптимізації продуктивності та довговічності.
Ресурси:
Що таке електрична шина? Види, переваги, недоліки
Системи шин: плюси і мінуси для розподілу електроенергії
Шинопровод: встановлення, пояснення переваг і недоліків
Тел.: +86-577-88671000
Електронна адреса: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Адреса: кімната № 1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center, Station Road, Веньчжоу, Китай
ЗАПИТАЙТЕ ЦІНУ
WhatsApp нас
 : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 англійська
англійська Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська турецька
турецька Polski
Polski Нідерланди
Нідерланди Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย монгол
монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά


