Fusibile per sistema di energia solare
29 marzo 2025
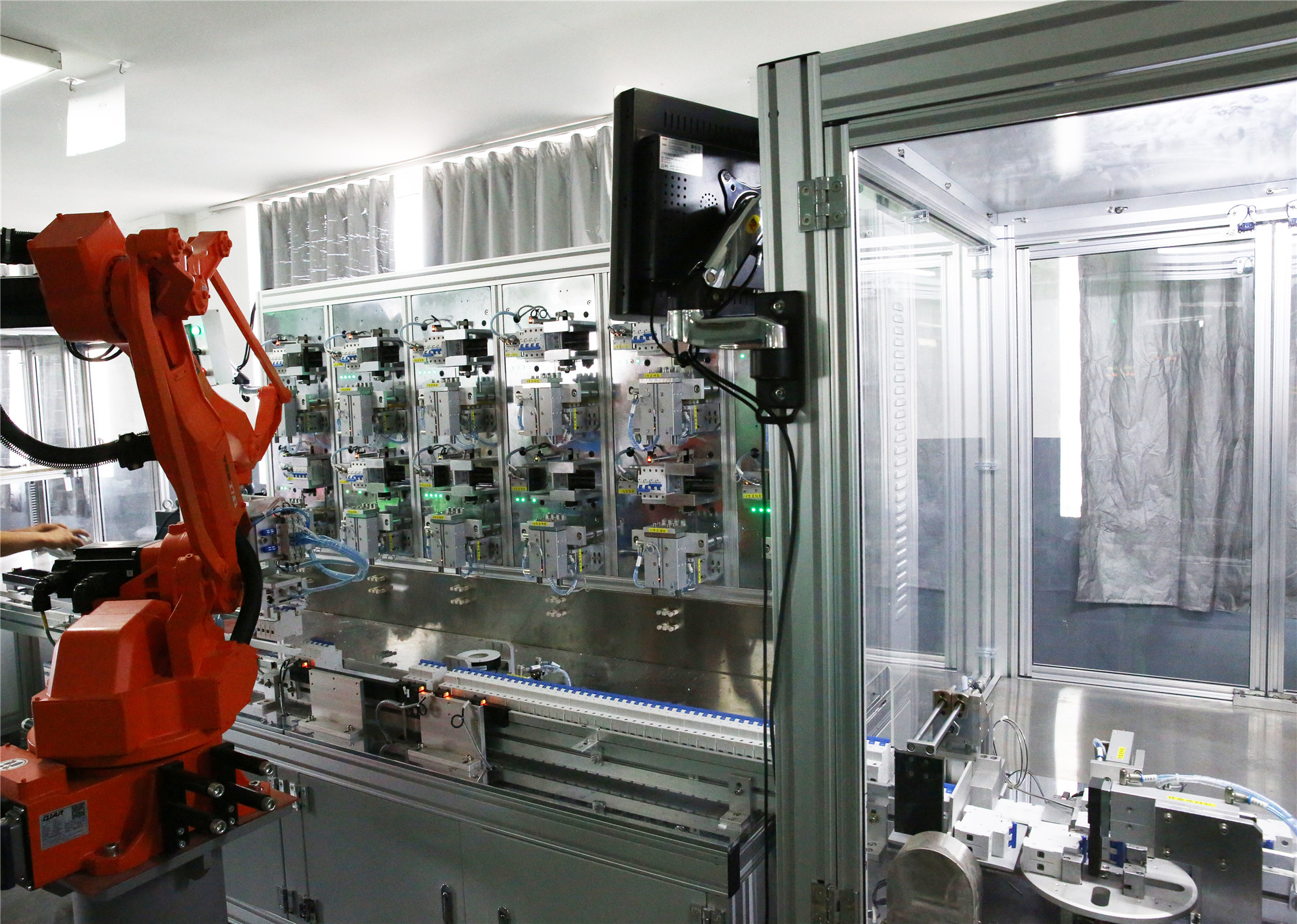
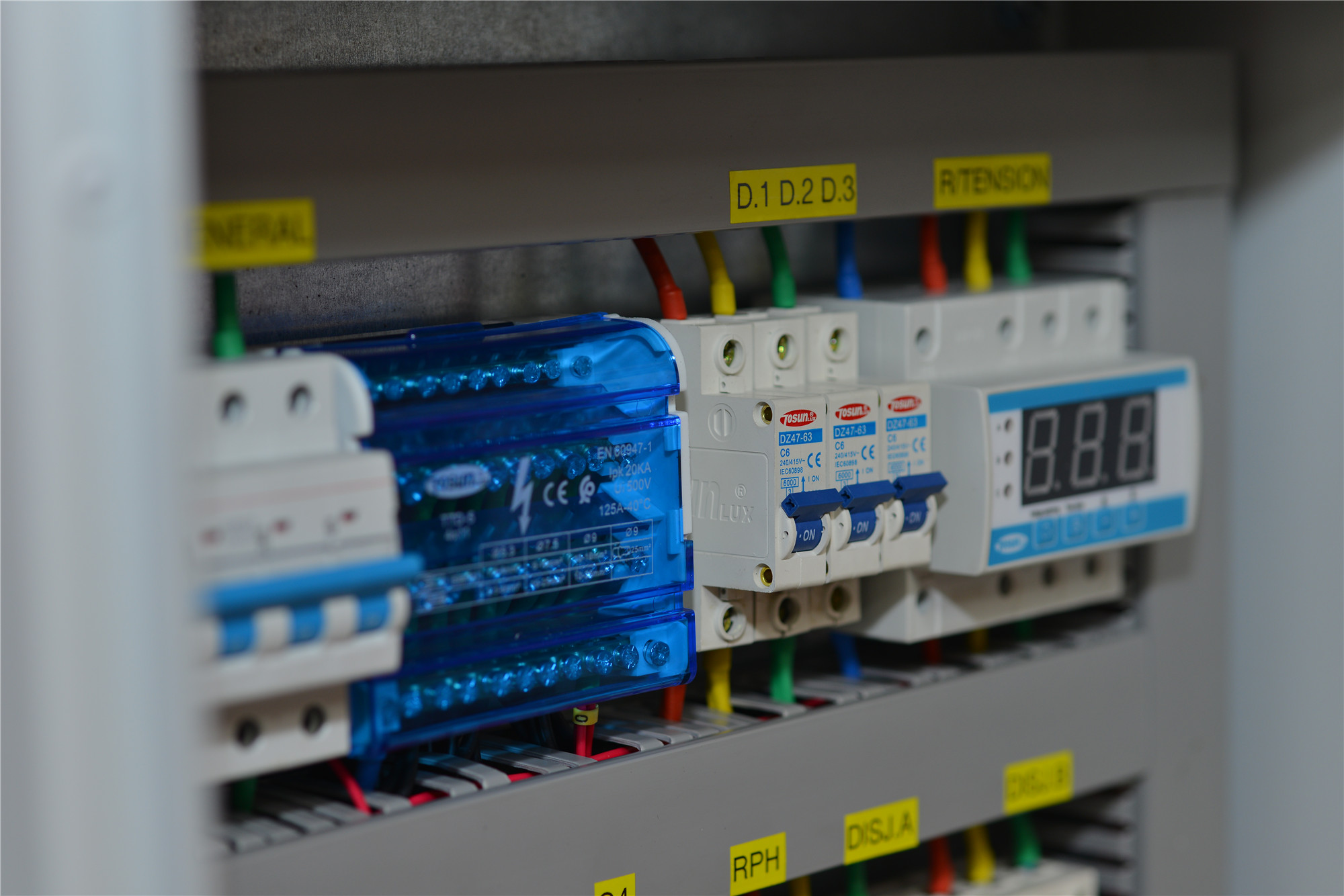
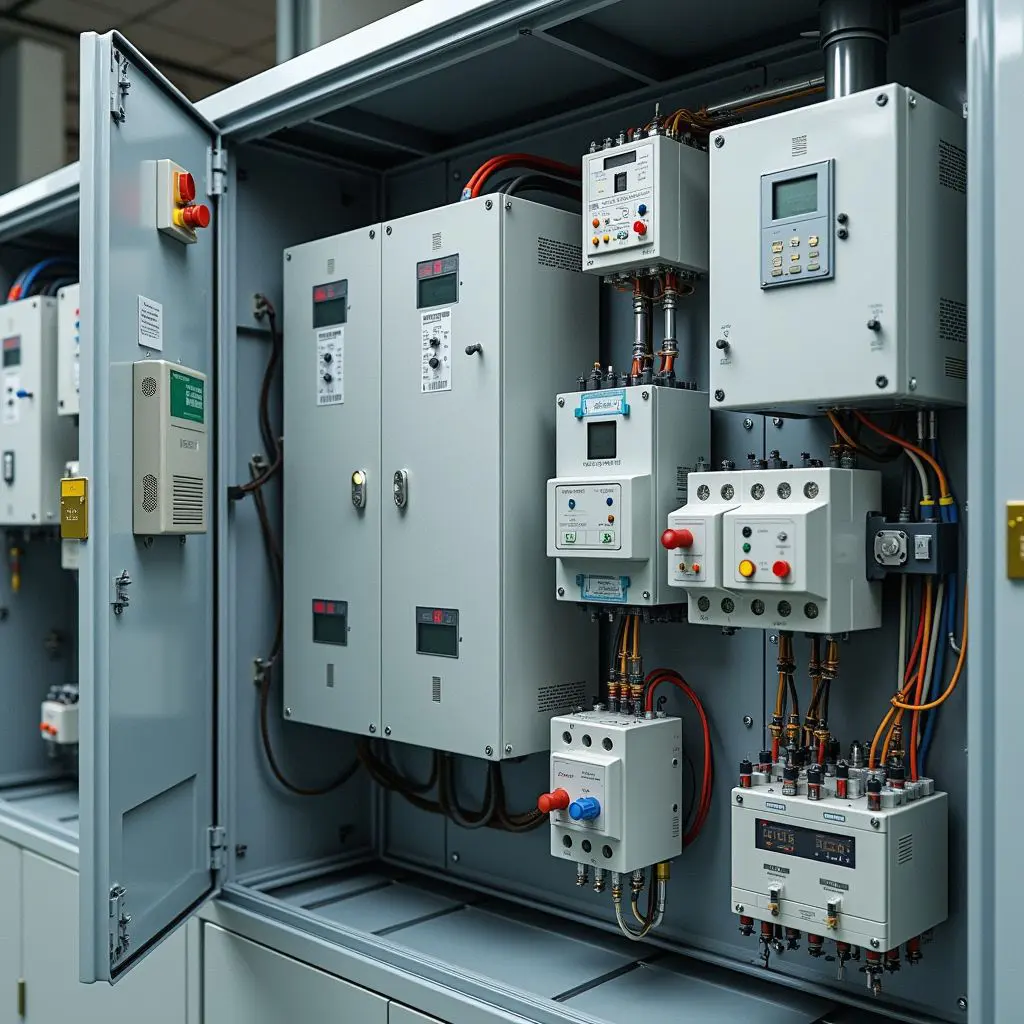
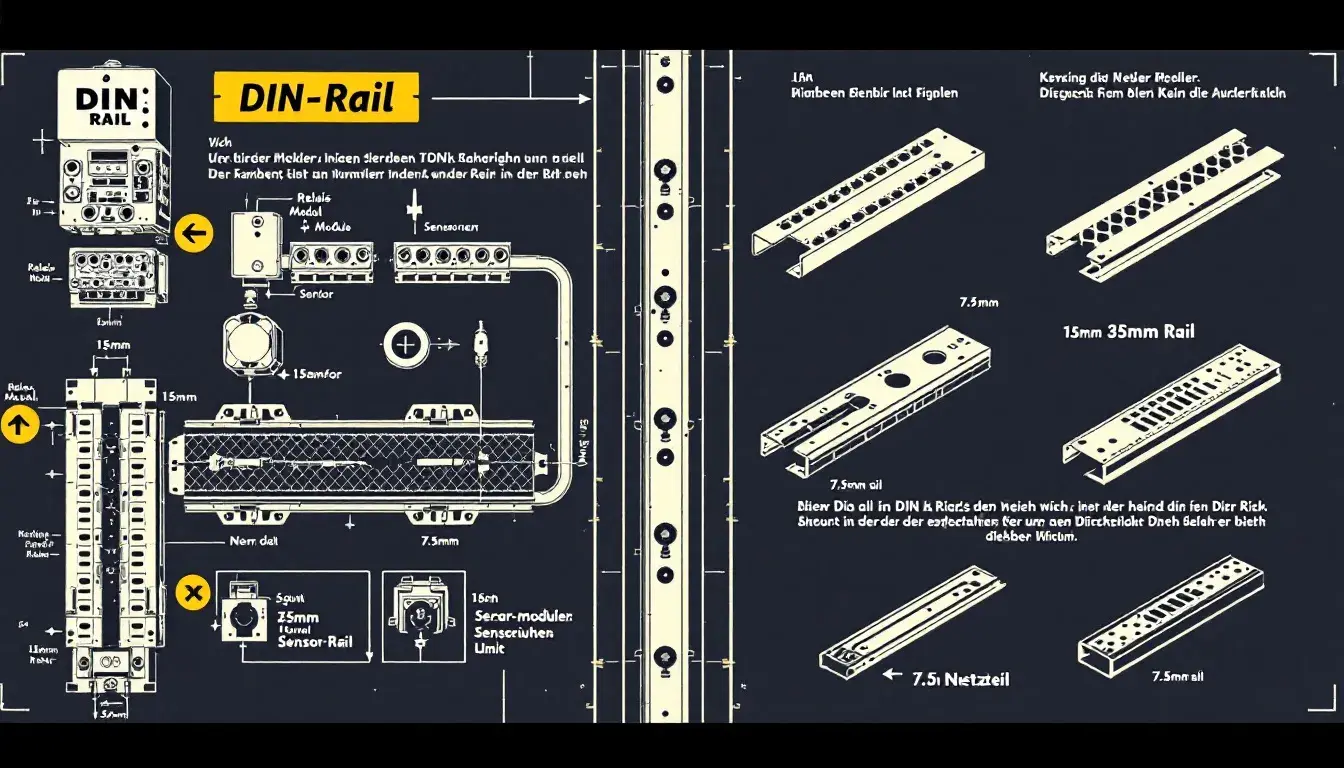
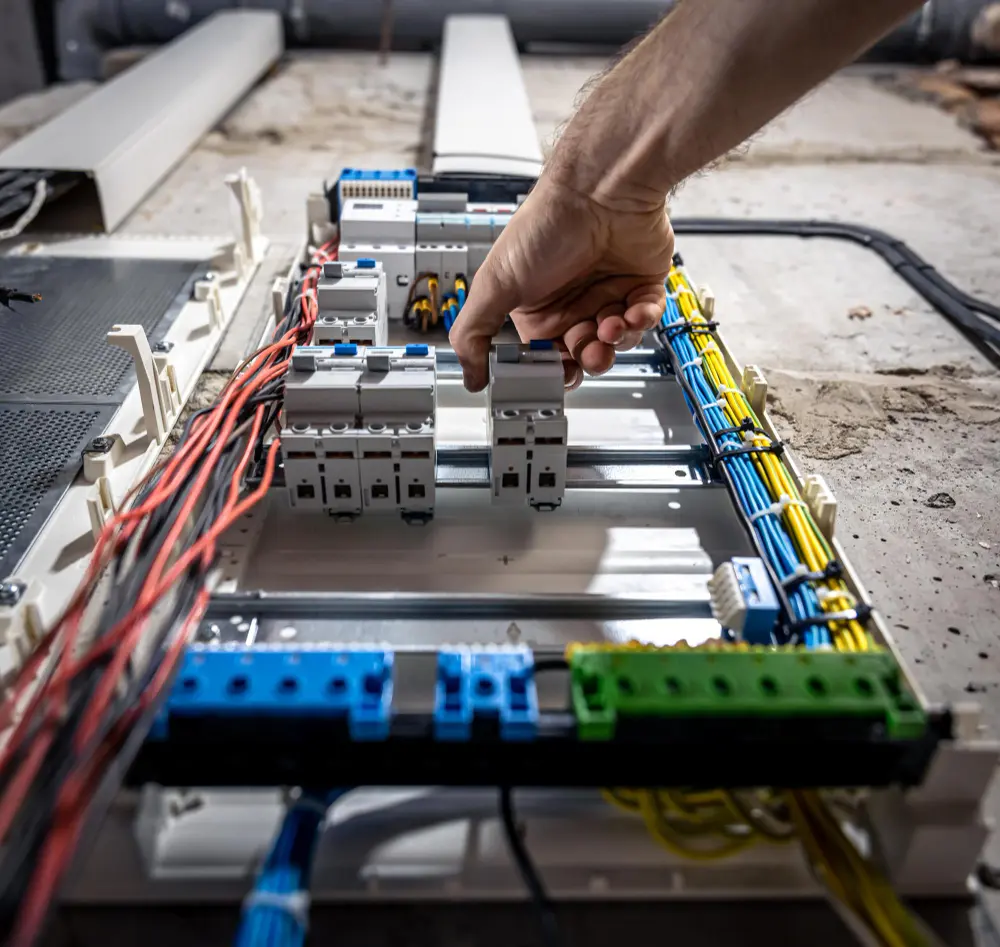
Per garantire la sicurezza e l'efficienza del tuo impianto solare, inizia da un componente chiave: la scatola dei fusibili CC solare. Questo articolo spiega il ruolo della scatola dei fusibili CC solare nella protezione del tuo impianto solare dai pericoli elettrici. Imparerai come selezionare il fusibile giusto, installarlo correttamente e mantenerlo per far funzionare il tuo impianto senza problemi. Punti chiave Le scatole dei fusibili CC sono essenziali per proteggere gli impianti fotovoltaici solari da correnti eccessive e cortocircuiti, garantendo sicurezza e longevità. La selezione del tipo e della classificazione del fusibile appropriati in base alle specifiche dei componenti, alle classificazioni della corrente e ai fattori ambientali è fondamentale per mantenere l'integrità del sistema. La manutenzione e le ispezioni regolari dei fusibili CC migliorano la sicurezza, prevengono guasti imprevisti e prolungano la durata dei componenti elettrici solari. Informazioni sulle scatole dei fusibili CC per impianti solari Scatole dei fusibili CC: essenziali per la sicurezza dell'impianto fotovoltaico solare Scopo: le scatole dei fusibili CC sono essenziali per proteggere il tuo impianto fotovoltaico solare. Prevengono correnti eccessive e cortocircuiti, che possono causare danni e potenziali incendi. Funzione: i fusibili e gli interruttori salvaguardano il cablaggio e i dispositivi del tuo impianto dal surriscaldamento, garantendo la sicurezza e la longevità del tuo investimento. Componenti: Blocco fusibile CC: essenziale per mantenere l'integrità del sistema. Portafusibile: importante per fissare i fusibili in posizione. Tipi di fusibili: fusibili ANL: adatti per unità più grandi grazie alla loro maggiore capacità di corrente. Fusibili a lama: ideali per carichi più piccoli. Protocolli di sicurezza: sono necessarie rigide linee guida di sicurezza per prevenire rischi elettrici. Scegli i fusibili in base al tipo di batteria per evitare guasti, poiché batterie diverse potrebbero reagire in modo diverso. Manutenzione: ispezioni regolari per danni […]
Per saperne di più : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 Inglese
Inglese Spagnolo
Spagnolo Russo
Russo Francese
Francese arabo
arabo Portoghese del Brasile
Portoghese del Brasile Ucraino
Ucraino Turco
Turco Polacco
Polacco Paesi Bassi
Paesi Bassi Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Hindi
Hindi اردو
اردو sfacciato
sfacciato Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Mongolo
Mongolo Fascino
Fascino Squalo
Squalo Ellenico
Ellenico