Solid State Relay vs Electromechanical Relay: What’s the Difference?
Table of Contents
ToggleRelays are small but crucial devices in electrical systems. They work like automatic switches, controlling circuits by turning them on or off.
Two popular types of relays are solid-state relays (SSRs) and electromechanical relays (EMRs). While both serve similar purposes, they differ in how they operate and their ideal uses.
Solid state relay vs electromechanical Relay—which is better?
What is a Solid-State Relay?
A solid-state relay (SSR) is a modern type of relay that uses electronic components instead of mechanical parts to control the flow of electricity. It relies on semiconductors, like thyristors or transistors, to switch electrical circuits on or off. SSRs are known for their durability and high-speed operation.
Unlike traditional relays, SSRs don’t have moving parts. This makes them much quieter and more reliable over time. They are perfect for applications where frequent switching is needed, such as in industrial automation or temperature control systems.
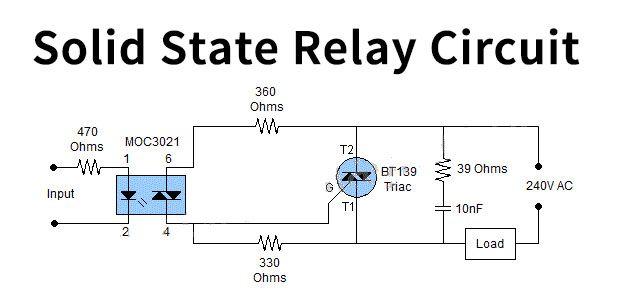
Key Features of Solid-State Relays
- Durability: No moving parts mean a longer lifespan and less maintenance.
- Silent Operation: Unlike mechanical relays, SSRs make no clicking noise during operation.
- Fast Switching: SSRs can switch on and off almost instantly, making them ideal for precision tasks.
- Compact Design: They are lightweight and easy to install in tight spaces.
What is an Electromechanical Relay?
An electromechanical relay (EMR) is a traditional relay that uses mechanical parts to complete its switching action. It has a coil that, when energized, creates a magnetic field to move a metal arm. This arm either opens or closes the circuit.
EMRs are straightforward and cost-effective, but their moving parts wear out over time. They are best for handling high electrical loads or when physical separation between circuits is needed. Despite being older technology, they remain popular due to their simplicity and affordability.
Key Features of Electromechanical Relays
- High Current Handling: EMRs are excellent for managing larger electrical loads.
- Physical Separation: The mechanical components create a clear separation between circuits, adding safety.
- Budget-Friendly: EMRs are cheaper than SSRs, making them a common choice for many applications.
- Reliable for Low-Switching Applications: Ideal for projects with limited switching requirements.
Solid State Relay vs. Electromechanical Relay: Key Differences
To help you understand which relay is right for your project, let’s break down the differences:
| Feature | Solid State Relay (SSR) | Electromechanical Relay (EMR) |
| Operation | Uses semiconductors to switch electricity | Uses a coil and moving parts to switch electricity |
| Durability | Long-lasting due to no moving parts | Shorter lifespan due to wear and tear on moving parts |
| Switching Speed | Extremely fast; great for precise control | Slower due to mechanical movement |
| Noise | Silent operation | Produces a clicking sound when switching |
| Current Capacity | Limited ability to handle very high currents | Excellent for high current loads |
| Cost | More expensive upfront | Cheaper and widely available |
| Applications | Ideal for industrial automation, temperature control | Best for household appliances, power distribution |
Applications of Solid State Relays
Solid-state relays are ideal for situations requiring quick, silent, and frequent switching. Here are some common uses:
Industrial Automation
SSRs can control complex machinery with precision, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
Temperature Control
Found in HVAC systems and industrial ovens, SSRs regulate heat or cooling systems effectively.
Lighting Systems
SSRs are used in smart lighting setups, especially for LEDs, because of their silent operation.
Electronics
In devices like computers or audio systems, SSRs provide precise and quiet switching.
Applications of Electromechanical Relays
Electromechanical relays are better suited for handling high current loads and situations where cost is a factor. Here are some examples:
Household Appliances
Devices like washing machines, microwaves, and air conditioners rely on EMRs for their simplicity and durability.
Power Distribution
EMRs are commonly used in power grids or industrial setups where managing large currents is critical.
Motor Control
For elevators, escalators, and heavy machinery, EMRs provide reliable switching.
Budget-Conscious Projects
EMRs are perfect for low-cost electrical solutions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Both SSRs and EMRs have their own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s look at them closely:
Advantages of Solid State Relays
- Durability: Lasts longer than mechanical relays.
- Silent Operation: Perfect for noise-sensitive environments.
- High-Speed Switching: Great for precision tasks.
Disadvantages of Solid State Relays
- Higher Cost: More expensive than EMRs.
- Heat Sensitivity: Requires cooling in some cases to avoid overheating.
- Limited Current Capacity: Not suitable for very high electrical loads.
Advantages of Electromechanical Relays
- High Current Handling: Can manage larger loads effectively.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable and widely available.
- Clear Circuit Separation: Offers safety and reliability.
Disadvantages of Electromechanical Relays
- Shorter Lifespan: Moving parts wear out with frequent use.
- Noisy Operation: Clicking sounds may not be ideal for quiet environments.
- Slower Switching: Less precise compared to SSRs.
Choosing the Right Relay
The choice between a solid-state relay and an electromechanical relay depends on your specific needs. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
Choose an SSR if your project needs a silent operation, frequent switching, or precise control. They are perfect for automation, electronics, and smart systems.
Choose an EMR if your project requires high current handling, budget-friendly components, or physical circuit separation. They are ideal for heavy-duty equipment and household appliances.
For example, if you’re building a factory automation system, go with an SSR for its speed and durability. If you’re working on a refrigerator or washing machine, an EMR would be more suitable due to its cost and high current capacity.
Conclusion
Relays are the backbone of many electrical systems, and understanding their differences is crucial for making the right choice.
By learning the key differences in solid state relay vs mechanical relay, you can choose the right relay for your project.
TOSUNlux offers a range of high-quality relays to meet your needs. Get a quote today and ensure your system operates efficiently and safely!
Tel: +86-577-88671000
E-mail: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Address: Room No.1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center,Station Road, Wenzhou, China
REQUEST A QUOTE
WhatsApp us
 : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά


