Single Phase vs Three Phase Electricity: Which is Best for You?
Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing between single phase vs three phase electricity depends on your power needs. This article compares the two, explaining their differences, advantages, and best uses.
Key Takeaways
- Single-phase power suits residential applications with simpler design and maintenance capabilities, handling loads up to 2,500 Watts efficiently.
- Three-phase power enables continuous and stable power delivery, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications that require higher loads and efficiency.
Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase power is crucial for selecting the appropriate system based on specific energy needs, particularly in energy-intensive environments like data centers.
Understanding Single Phase Power
Single-phase power is a basic component of electrical systems, consisting of a two-wire alternating current circuit with a phase wire and a neutral wire. The current alternates direction 50 to 60 times per second (AC), typically at a voltage of 230V and a frequency of 50 Hertz, making it ideal for household applications like lighting and heating.
Single-phase power is crucial in daily life due to its straightforward design, making it perfect for residential areas with low electrical power demand. Household appliances such as lights, refrigerators, and small heating systems depend on it, ensuring smooth and efficient home operations.
Advantages of Single Phase Power
Single-phase power offers several advantages, including simpler design and installation compared to three-phase systems, making it cost-effective for residential use. This simplicity also means easier maintenance and troubleshooting, benefiting homeowners and small businesses.
Single-phase power supplies are ideal for residential supplies, handling capacities up to 2,500 Watts. This is sufficient for common household appliances, ensuring efficient operation without complex and costly systems. Its straightforward nature makes it a practical everyday choice for a single phase power supply.
Disadvantages of Single Phase Power
However, single-phase power has drawbacks, notably its inefficiency for high-demand applications. It is unsuitable for running large electric motors or heavy machinery without additional equipment like motor starters or variable-frequency drives to manage heavy loads.
The need for additional equipment not only increases the complexity but also the cost of using single-phase power for high-demand applications. This inefficiency underscores the importance of choosing the right power system based on specific needs, especially when dealing with industrial or commercial settings that require substantial power.
How to measure single phase power
Measuring single-phase power involves understanding key electrical parameters. The fundamental formula for calculating single-phase power is kW = (Voltage × Current × Power Factor) ÷ 1,000. For straightforward applications where the power factor is not a concern, it simplifies to kW = (Voltage × Current) ÷ 1,000. To determine current draw for a known kilowatt load, use Current = 1,000 kW ÷ Voltage, ensuring your system can handle the load without overloading. For precise measurements, consider the root mean square (RMS) voltage and current with the formula P = Vrms × Arms. In circuits with reactive elements, include the power factor (cosø) in calculations.
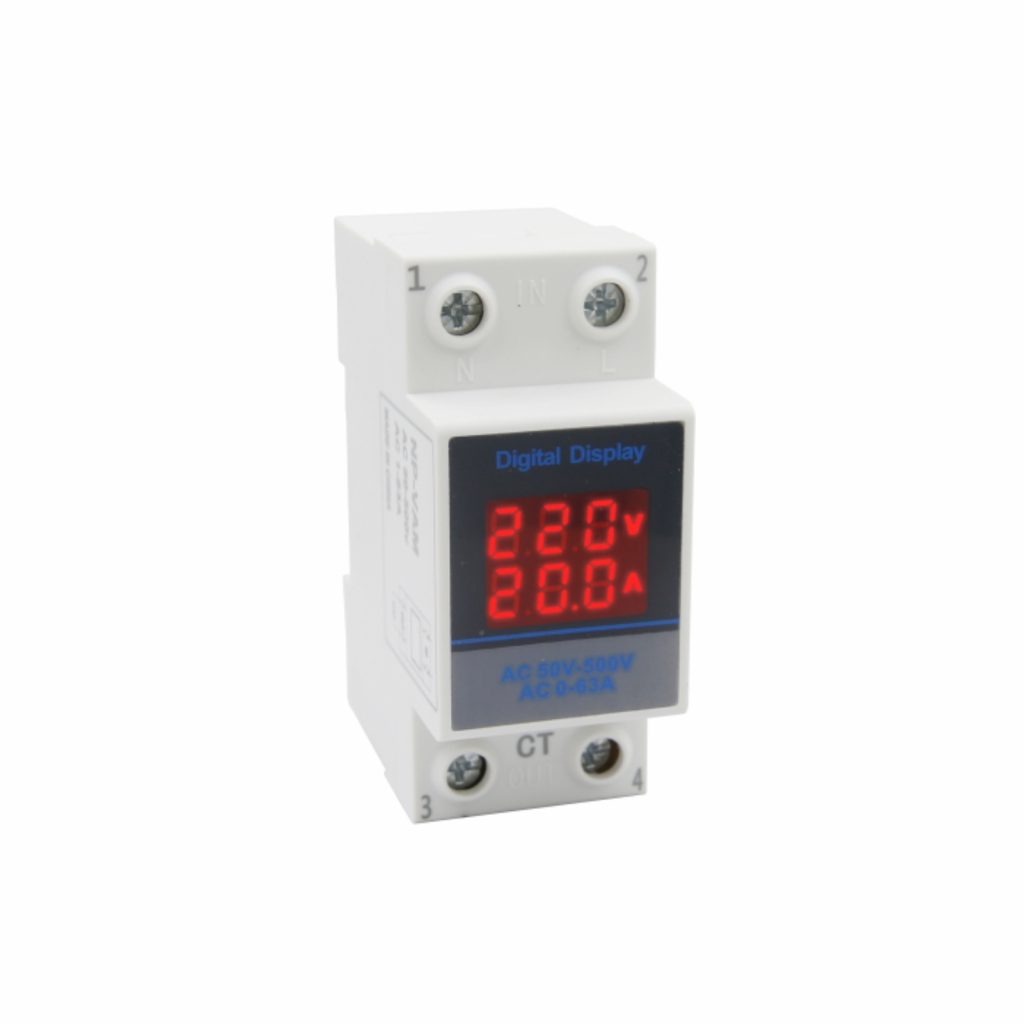
Designed for single-phase systems, the TOSUNlux power meter provides accurate measurement and monitoring of key electrical parameters such as active energy, reactive power, voltage, active power, power factor, apparent power, and current, ensuring both reliability and operational safety.
Exploring Three Phase Power

Three-phase power is a more complex and efficient form of alternating current that uses three wires. One of the primary advantages of a three-phase power supply is its ability to provide a continuous power supply, which is essential for high-demand applications. This type of power system typically uses three phase wires and sometimes a fourth neutral wire, along with a power wire. The configurations of a three-phase system can be either star (wye) or delta, with the star configuration including a neutral wire.
This continuous power supply makes three-phase systems perfect for heavy loads and demanding applications. Generators produce three AC electric currents in three-phase power, ensuring stable and efficient output.
The voltage generated between any two phases in a three-phase system is typically around 415V, providing the necessary power for industrial and commercial operations.
How Three Phase Power Works
In a three-phase system, the voltage is phase-shifted at 120 degrees, providing a stable power supply. This differs from single-phase power, where phases are angled at 180 degrees. Consequently, three-phase systems offer consistent power delivery, minimizing interruptions and voltage drops.
A major advantage of three-phase power is its efficiency, requiring less conductor material to transmit the same power as single-phase systems. This steady energy delivery makes it ideal for industrial applications requiring reliable power.
Applications of Three Phase Power
Three-phase power is better suited for commercial and industrial settings due to its ability to handle higher loads. It is essential for operating large electric motors and heavy machinery, making it the preferred choice in industries like manufacturing, construction, and data centers.
Conversely, single-phase power is used for residential applications like lighting, cooking, refrigeration, and small HVAC systems. While adequate for smaller loads, it lacks the capacity and efficiency for larger, demanding applications, emphasizing the need to choose the right power supply type.
Calculating Three Phase Power
Calculating power in a three-phase circuit uses the formula: P = V x I x √3. This accounts for line voltage, current, and the square root of three representing the phase shift. Multiplying these values determines the power output accurately.
This calculation is crucial for ensuring that the power system can handle the expected load without overloading the circuit. Understanding this formula and its application is essential for anyone working with three-phase power systems, whether in industrial settings or commercial operations.
Comparing Single Phase and Three Phase Power
The differences between single-phase and three-phase power systems are significant and impact their efficiency and applications. Below is a table highlighting the key differences:
|
Feature |
Single Phase Power |
Three Phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Wires | Two (one phase wire and one neutral wire) | Three phase wires, sometimes a fourth neutral wire |
| Voltage Delivery | Alternates direction 50 to 60 times per second | Phase-shifted at 120 degrees for stable delivery |
| Power Output | Suitable for residential applications up to 2,500 Watts | Ideal for industrial applications with continuous output |
| Efficiency | Less efficient for high-demand applications | More efficient, minimizes voltage drops and interruptions |
| Common Applications | Household appliances like lighting and refrigeration | Industrial equipment and large electric motors |
| Initial Torque for Motors | Insufficient for starting small single phase motors | Adequate for starting large three phase motors |
| Conductor Material | Requires more material for the same power transmission | Requires less conductor material, reducing costs |
| Use in Data Centers | Not typically used | Preferred for optimizing Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) |
This table clearly illustrates how three-phase systems allow for a more balanced distribution of electricity, which is crucial for minimizing losses in power distribution. This balance enhances power density, allowing for smaller wiring sizes and lower costs. Additionally, three-phase power provides a consistent and continuous power output, avoiding flicker and outages common in single-phase systems.
Data centers, in particular, benefit from using three-phase power due to its ability to optimize Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and enhance overall uptime. The shift to three-phase power in data centers is driven by increased power demands and the need for reliable operation during peak loads.
Converting Between Single Phase and Three Phase Power
Converting between single-phase and three-phase power is essential for running three-phase motors in areas lacking three-phase electrical infrastructure. One method is using a rotary phase converter, which employs an electric motor and generator to create balanced three-phase power from a single-phase source. This method is reliable and efficient for heavy-duty applications.
Static phase converters, which use capacitors for power conversion, are another option. Though they may not produce true three-phase output, they suit light applications. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) convert single-phase AC to DC and back to three-phase AC, offering frequency and voltage control, making them versatile.
Safety measures are critical during the conversion process. Turning off the main power before conversion and ensuring proper grounding are essential steps to prevent accidents and ensure a safe conversion.
The Role of Power Distribution Systems
Power distribution systems are crucial for efficiently managing the load and delivery of both single-phase and three-phase electricity. These systems ensure that electricity is delivered safely and efficiently, enabling households and industries to function properly.
Three-phase power is widely used for generating and distributing electricity across grids. Its capacity to handle higher loads and provide consistent power makes it essential for modern three phase supply and three phase power system distribution systems.
Why Data Centers Prefer Three Phase Power
Data centers need a reliable power supply for continuous critical operations. Three-phase power is preferred for its efficiency in delivering higher power, ensuring maximum efficiency and reliability.
Three-phase power is essential for data centers due to rising power demands and the potential impact of interruptions. It supports critical functions, making it indispensable.
Summary
In conclusion, both single-phase and three-phase power systems have their unique advantages and applications. Single-phase power is simple and ideal for residential use, while three-phase power offers efficiency and reliability for commercial and industrial applications. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions about your power needs.
Whether you’re a homeowner or a business owner, choosing the right power system can enhance your operations and ensure a stable power supply. Embrace the power of knowledge and make the best choice for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between single-phase and three-phase power?
The main difference between single-phase and three-phase power is the number of wires and their application; single-phase uses two wires and is suited for residential use, while three-phase employs three or four wires, making it more efficient for handling higher loads in commercial and industrial settings.
Why is three-phase power more efficient than single-phase power?
Three-phase power is more efficient than single-phase power because it delivers a continuous power supply with consistent voltage, minimizing interruptions and voltage drops. Additionally, it requires less conductor material for transmission in high-demand scenarios, making it a cost-effective solution for various applications.
Can single-phase power be converted to three-phase power?
Yes, single-phase power can be converted to three-phase power using rotary phase converters, static phase converters, or Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), allowing you to operate three-phase machinery in areas without three-phase infrastructure.
What are the common applications of single-phase power?
Single-phase power is primarily utilized for residential applications such as lighting, cooking, refrigeration, and small HVAC systems due to its suitability for low-demand needs and ease of installation and maintenance.
Why do data centers prefer three-phase power?
Data centers prefer three-phase power due to its ability to deliver higher efficiency and reliability, which is essential for supporting critical applications and managing increased power demands. The continuous supply of power is vital for uninterrupted operations.
Tel: +86-577-88671000
E-mail: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Address: Room No.1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center,Station Road, Wenzhou, China
REQUEST A QUOTE
WhatsApp us
 : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά



