Top 5 DC Isolator Switch Brands for Solar PV Systems
22nd Jul 2025
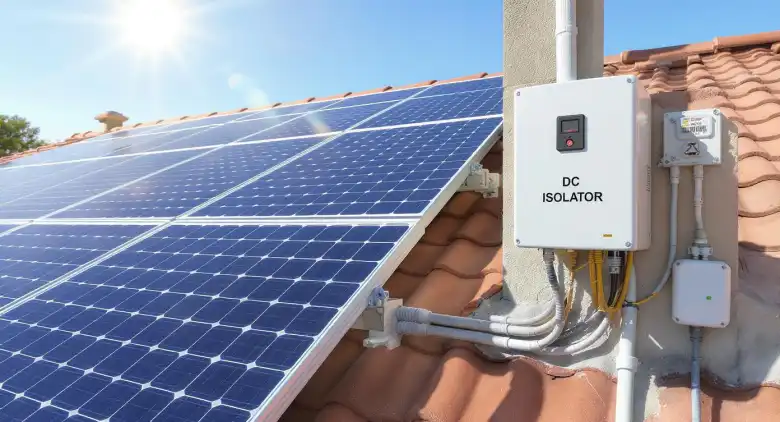
When you think about building or upgrading a solar PV system, safety and performance should be at the top of your list. One of the most critical components that keeps your solar installation safe and efficient is the solar isolator switch. This essential device disconnects the DC power from solar panels to the inverter, allowing for safe maintenance and emergency shutdowns. In this guide, we’ll dive into what makes a good solar panel DC isolator switch, explore the best brands on the market today, and help you make the right choice for your project. Whether you’re a homeowner, installer, or solar enthusiast, understanding the DC isolator switch is key to ensuring your system runs smoothly and safely. Key Criteria for Selecting a High-Quality PV Isolation Switch Choosing the right PV isolation switch (another term for a solar isolator switch) isn’t just about price; it’s about matching safety, durability, and performance to your system needs. A good solar isolator switch must handle the maximum voltage and current of your solar setup. Many solar panel DC isolator switches today support up to 1,500V DC and 32A or higher, which is crucial for high-power systems. Unlike AC, DC circuits do not naturally cross zero voltage, making them more difficult to disconnect safely. Advanced DC isolator switches use arc suppression techniques, such as magnetic blowouts or special contact designs, to safely interrupt current flow and avoid fire risks. Most PV isolation switches are installed outdoors and must withstand harsh weather. A high-quality solar isolator switch typically carries an IP66 […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά