Top 10 Electrical Equipment Suppliers in China
21st Mar 2025
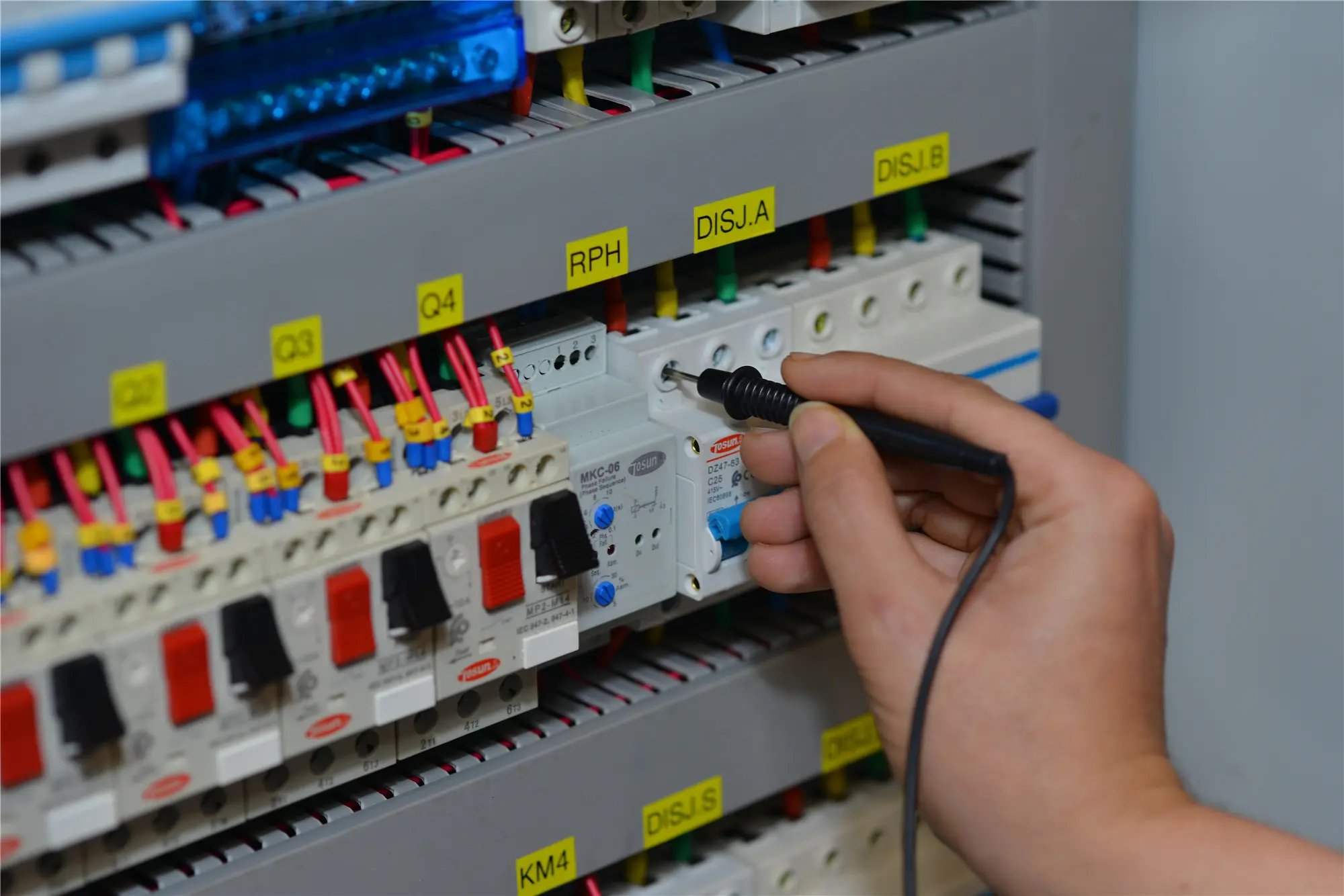
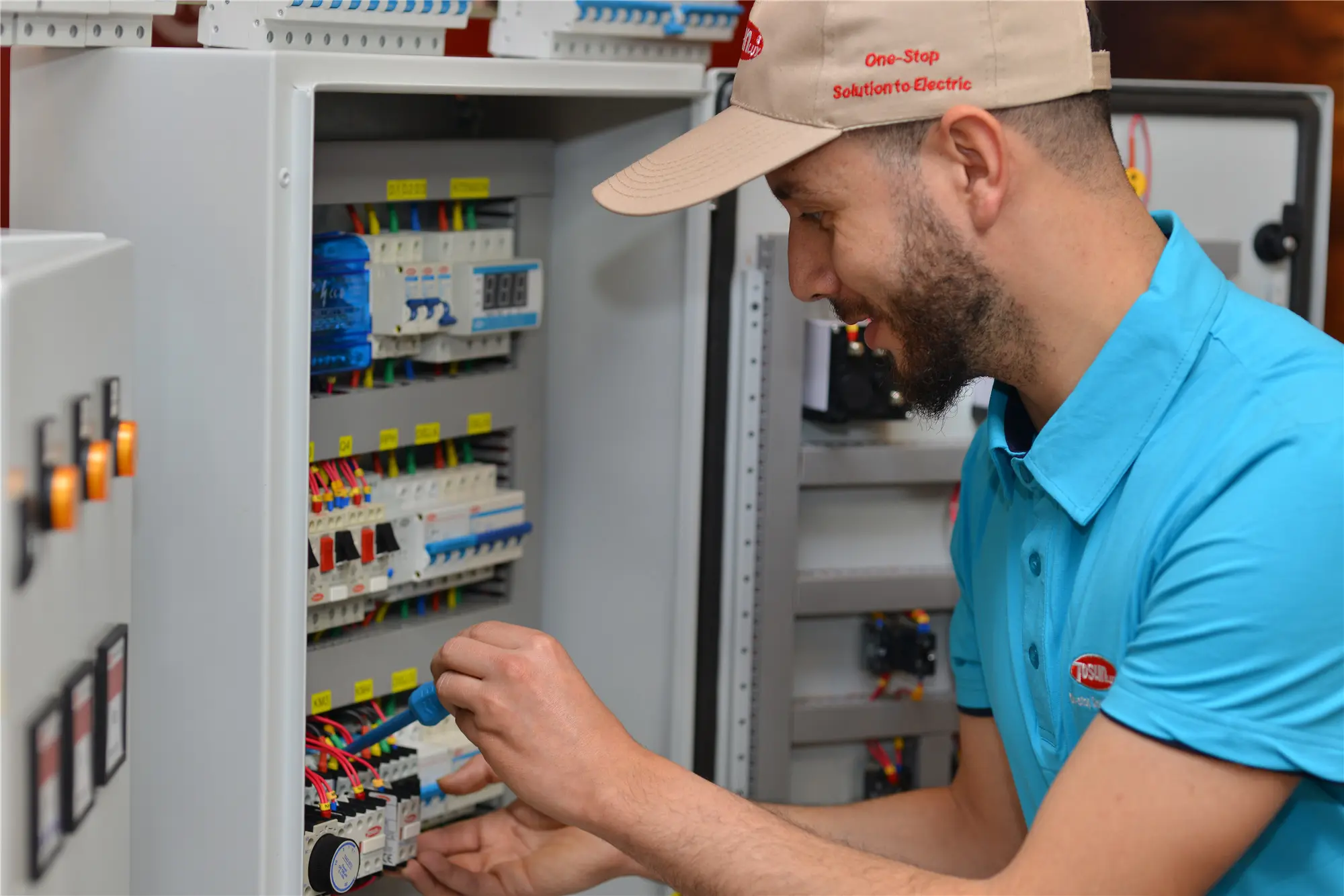
Undoubtedly, China has emerged as a global powerhouse in the electrical equipment industry. The Asian giant boasts a diverse array of companies that lead in innovation, sustainability, and technological prowess, helping engineers and designers find the right products and solutions for their specific projects. Below are the top 10 electrical equipment suppliers in China that represent the forefront of global industrial technology. The Global Electrical Equipment Industry Landscape The global electrical equipment industry is vast and dynamic, playing a crucial role in powering the world. It includes companies that manufacture products like transformers, circuit breakers, and batteries, which are essential for energy distribution and management. Key Highlights Market Size: The industry is valued at over $100 billion and continues to grow as demand for energy-efficient solutions rises. Major Players: Leading companies such as Siemens, General Electric, and Schneider Electric dominate the market, known for their innovation and reliability. Growth Drivers: Factors like urbanization, industrialization, and the shift towards renewable energy sources drive the industry’s expansion. Employment: The industry employs millions globally, contributing significantly to economic growth and development. Technology and Innovation: Advancements in technology, such as smart grids and energy storage systems, are transforming how electrical equipment is used. List Top 10 Electrical Equipment Suppliers Rank Supplier Name Founding Year Website Key Products 1 CHINT Group, Inc. 1984 chintglobal.com Low-voltage power distribution units, circuit breakers 2 DELIXI Electric, Inc. 1984 www.delixi-electric.com/en Power distribution products, industrial control products 3 People Electric 1996 https://www.peopleelectric.com/ Distribution equipment, transformer, low-voltage products 4 China Aviation Lithium Battery 2009 http://en.calb-tech.com/ Battery […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά