How Does Fuse Holder Work?
25th Mar 2025
This guide explains the basic principles of fuses and fuse holders, making it easy for beginners to understand their function in electrical circuits.
Read More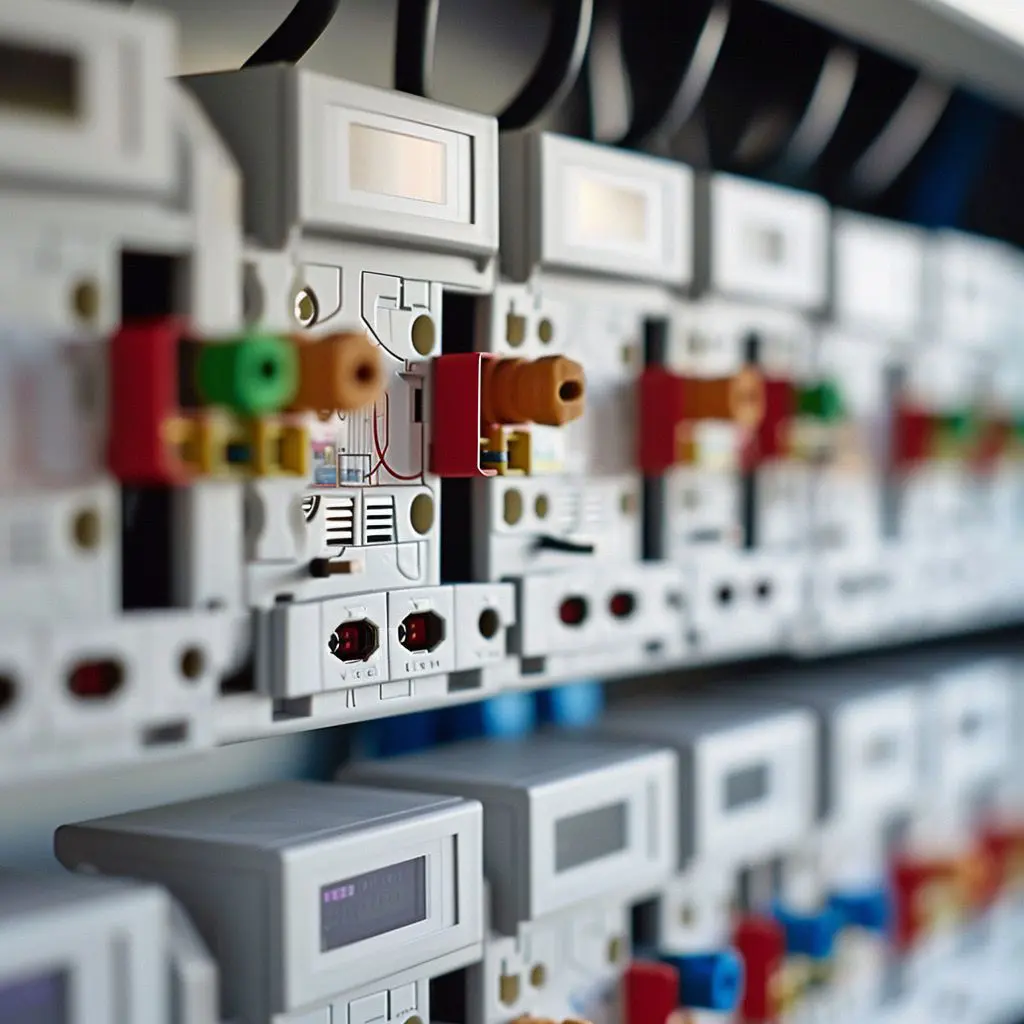
This guide explains the basic principles of fuses and fuse holders, making it easy for beginners to understand their function in electrical circuits.
Read More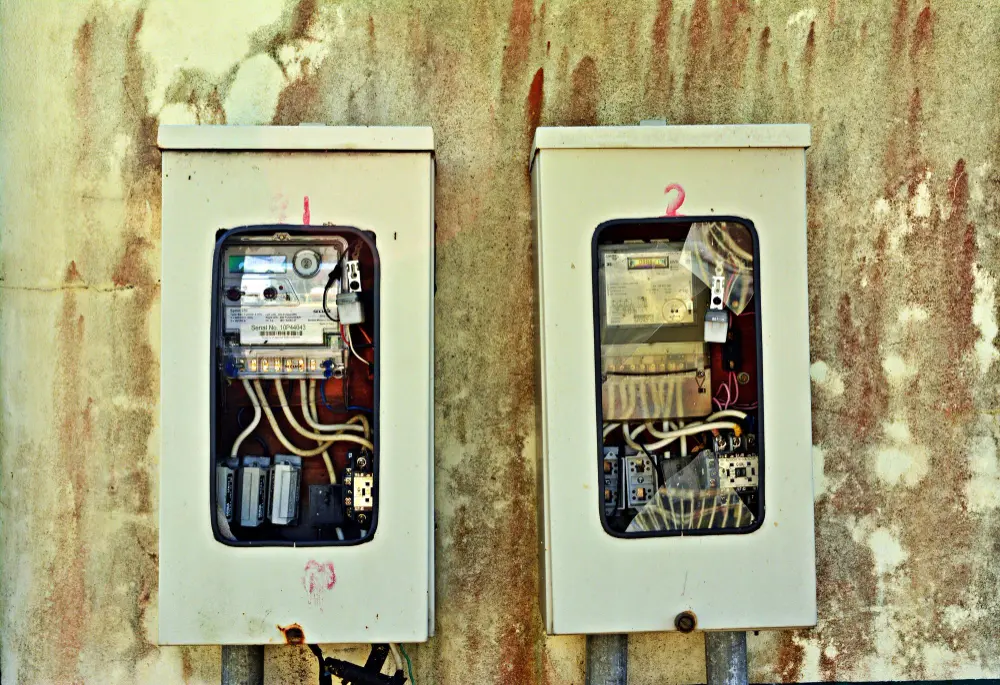
Did you know that the right electrical box can prevent dangerous electrical fires? With over 12 types of electrical boxes on the market, choosing the right one for your electrical devices can be overwhelming. This guide will help you navigate through the options with ease. We’ll cover essential topics such as the different sizes, materials, and styles of electrical boxes, including metal and plastic options. You’ll learn how to select the best box for your needs, whether it’s for outlets, switches, or ceiling fans. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to make safe and efficient choices for your home’s electrical system. Let’s ensure your wiring is both secure and effective. How Do I Choose an Electrical Box? Choosing the right electrical box is essential for safety and efficiency in your home. Here’s a simple guide to help you make the best choice: 1. Types of Electrical Boxes Round Boxes: Perfect for ceiling lights and smoke alarms. Ceiling Boxes: Designed for lightweight ceiling-mounted lights and devices like smoke alarms. Not suitable for heavy fixtures like ceiling fans. Square Boxes: Ideal for junction boxes and wiring connections. Rectangular Boxes: Commonly used for switches and outlets. Outlet Box: Used for outlets and can sometimes serve the same function as a junction box. Important to consider the type of cable and whether the installation is for new or old work. 2. Styles Single Gang Boxes: Suitable for one device like a switch or outlet. Double Gang Boxes: Used when you need two switches or outlets. 3. Materials Metal […]
Read More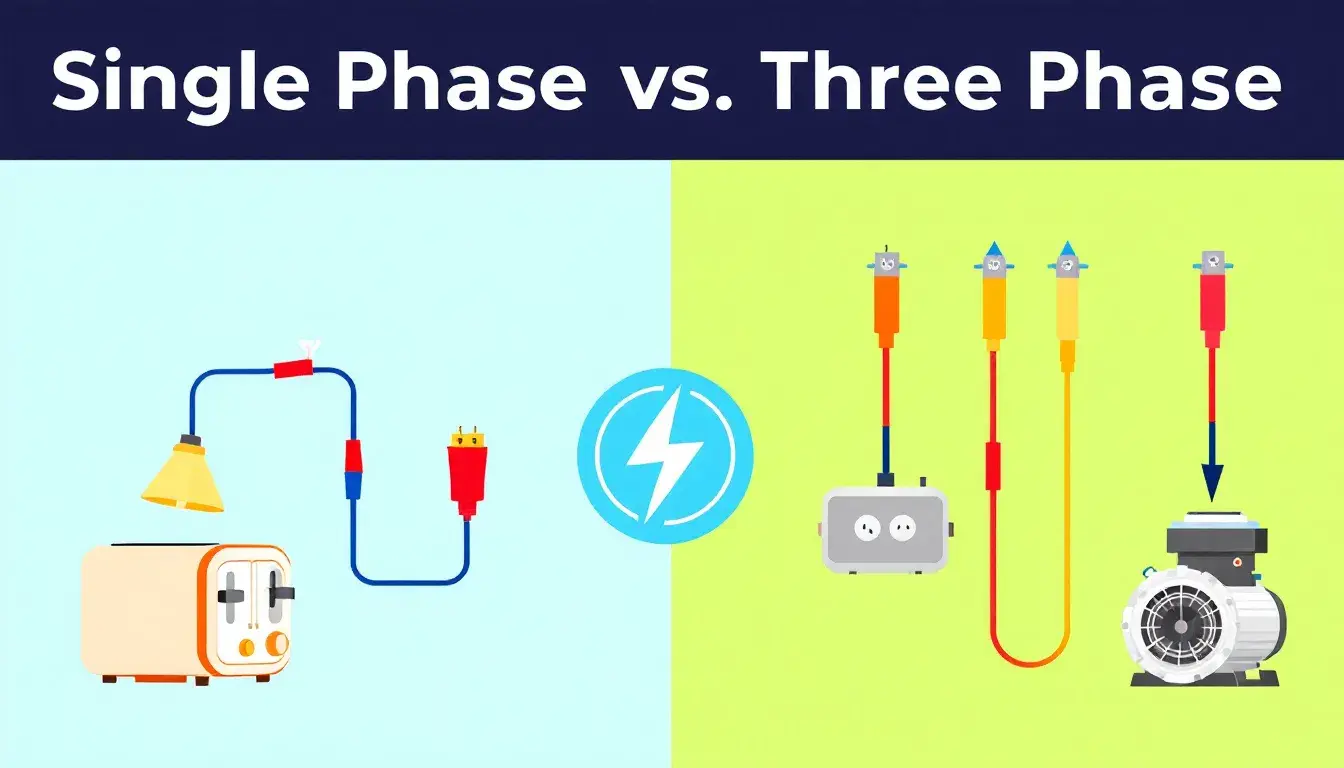
Choosing between single phase vs three phase electricity depends on your power needs. This article compares the two, explaining their differences, advantages, and best uses. Key Takeaways Single-phase power suits residential applications with simpler design and maintenance capabilities, handling loads up to 2,500 Watts efficiently. Three-phase power enables continuous and stable power delivery, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications that require higher loads and efficiency. Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase power is crucial for selecting the appropriate system based on specific energy needs, particularly in energy-intensive environments like data centers. Understanding Single Phase Power Single-phase power is a basic component of electrical systems, consisting of a two-wire alternating current circuit with a phase wire and a neutral wire. The current alternates direction 50 to 60 times per second (AC), typically at a voltage of 230V and a frequency of 50 Hertz, making it ideal for household applications like lighting and heating. Single-phase power is crucial in daily life due to its straightforward design, making it perfect for residential areas with low electrical power demand. Household appliances such as lights, refrigerators, and small heating systems depend on it, ensuring smooth and efficient home operations. Advantages of Single Phase Power Single-phase power offers several advantages, including simpler design and installation compared to three-phase systems, making it cost-effective for residential use. This simplicity also means easier maintenance and troubleshooting, benefiting homeowners and small businesses. Single-phase power supplies are ideal for residential supplies, handling capacities up to 2,500 Watts. This is sufficient for common household […]
Read More
Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs) are vital for electrical safety. They detect leakage currents and disconnect circuits to prevent electric shocks and fires. This article explores RCCB uses in homes, commercial buildings, and industrial settings, highlighting their role in protecting both people and equipment. Key Takeaways RCCBs provide essential protection against electric shocks and fire hazards by detecting leakage currents and automatically disconnecting faulty circuits. In commercial and industrial settings, RCCBs enhance safety by preventing damage to equipment, minimizing downtime, and ensuring compliance with electrical safety standards. Selecting the appropriate RCCB involves considering factors such as sensitivity, rating, and compatibility with existing electrical systems, emphasizing the need for proper installation by qualified professionals. What is RCCB Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs) are pivotal devices in the realm of electrical safety. Their primary function is to detect and disconnect electrical circuits whenever they sense a leakage current, thereby preventing potential electric shocks and fire hazards. The internal mechanism of an RCCB operates on the working principle of detecting an imbalance between the live and neutral wires, which signifies a leakage current. A residual current device is essential for enhancing electrical safety. The importance of RCCBs in electrical safety cannot be overstated. They provide an essential layer of protection that traditional circuit breakers might miss. RCCBs protect both people and equipment from electrical malfunctions by disconnecting the circuit as soon as a fault is detected. Common Uses of RCCB Ensuring Safety in Commercial Buildings In commercial buildings, the safety of personnel and equipment is crucial. RCCBs enhance […]
Read More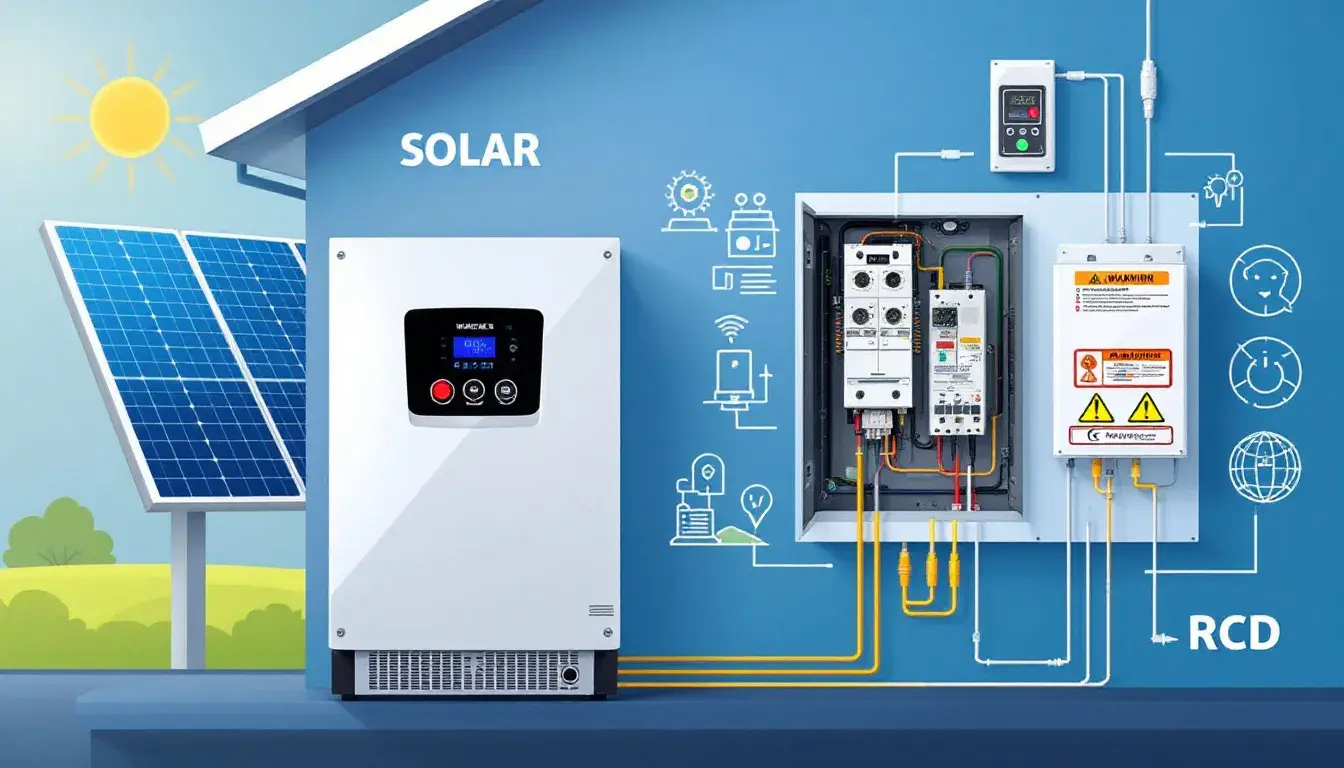
An RCD current device quickly disconnects power to prevent electric shocks and fires when it detects a fault. In this article, we explain what RCDs are, why they are vital for solar inverter systems, and how to choose the right one. Key Takeaways Residual Current Devices (RCDs) protect against electric shock and electrical fires by detecting leakage currents and disconnecting the circuit quickly. In solar inverter systems, RCDs must be capable of detecting DC residual fault currents, as traditional AC RCDs may not function properly in the presence of DC leakage. Type B RCDs are particularly suitable for solar installations due to their ability to handle DC fault currents, while Type A RCDs can serve mixed loads but may not provide the same level of protection. What is an RCD Current Device? A Residual Current Device (RCD) is a crucial safety tool in electrical systems, designed to: Prevent Electric Shocks: Quickly disconnects the circuit when it detects a leakage current. Reduce Fire Risks: Helps prevent electrical fires by acting swiftly on fault detection. How Does an RCD Work? Constant Monitoring: It continuously checks the balance of electrical current flowing through the live and neutral wires. Detecting Imbalances: Normally, the current entering through the live wire should equal the current returning via the neutral wire. An imbalance indicates a potential leakage, often through a person, which can cause electric shocks. Rapid Response: Upon detecting a leakage current, the RCD cuts off the power supply in about 30 milliseconds, significantly reducing the risk of injury or fire. […]
Read More
Looking for the symbol for a contactor? Understanding this symbol is crucial for reading and interpreting electrical diagrams accurately. In this article, we’ll not only show you the symbol but also dive into choosing, testing, and troubleshooting AC contactors effectively. How to Choose a AC Contactor Choosing the right AC contactor is key for your AC unit to work well and last long. Here’s a simple guide to help you make the right choice: Match the Voltage: Ensure the contactor’s voltage rating matches your system’s maximum voltage. For example, if your AC unit operates at 240 volts, choose a contactor rated for at least 240 volts to avoid overloading. Check the Current Rating: The contactor should handle more than the load current and the initial surge current. For instance, if your compressor and motor draw 30 amps, opt for a contactor with a rating of at least 40 amps to manage high inrush currents safely. Select the Right Pole Configuration: AC contactors come in different configurations like 2-pole, 3-pole, and 4-pole. A 3-pole contactor is ideal for three-phase loads, while a 4-pole contactor might be needed for more complex setups. Consider Lifespan: Look for a contactor with a long mechanical and electrical lifespan. This ensures it can handle many cycles before needing replacement, saving you time and money in the long run. Fit and Size: Make sure the contactor fits your control panel. Measure your panel space and check the contactor dimensions before purchasing. Budget and Quality: Compare prices from different manufacturers. Choose a contactor […]
Read More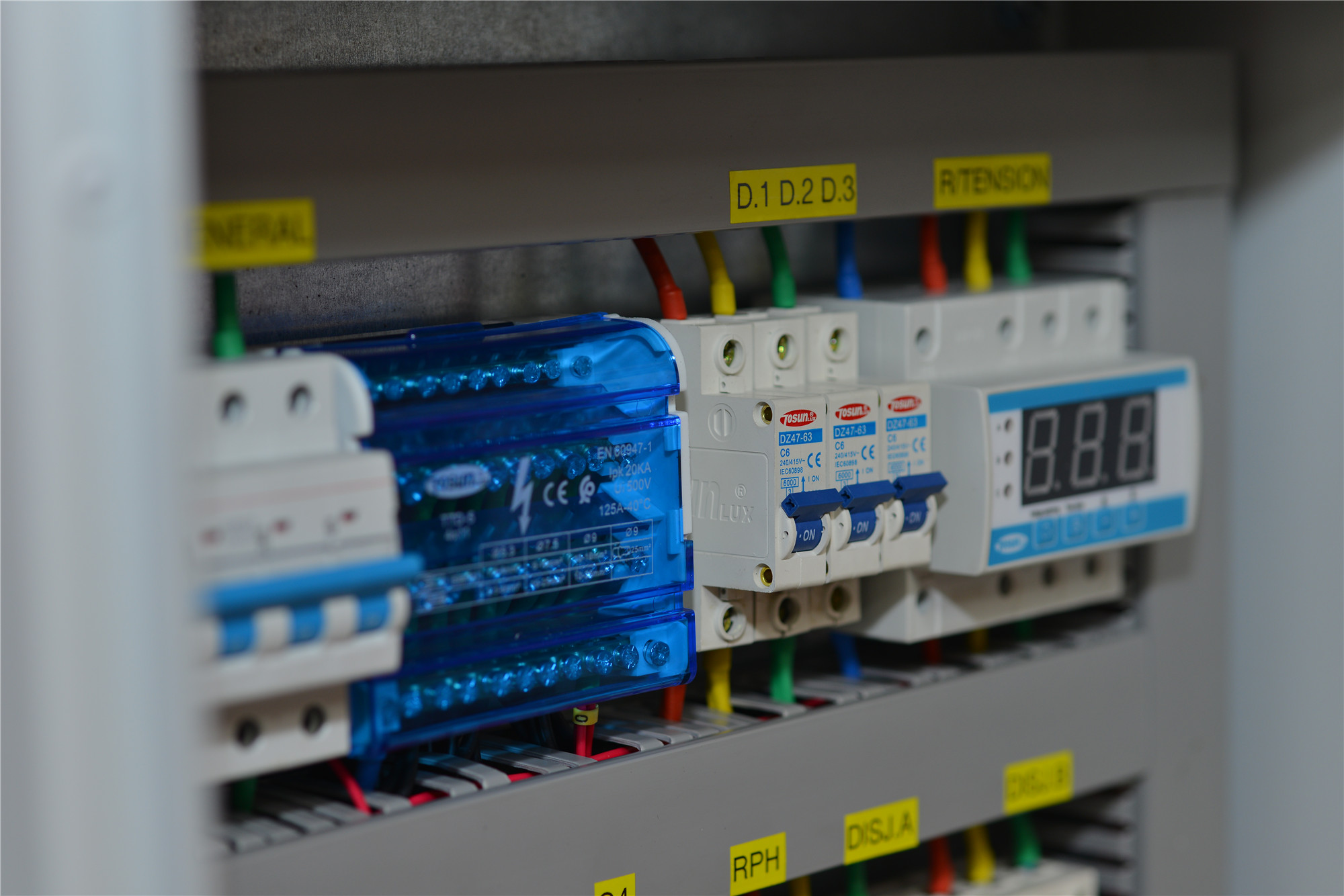
An electric generator automatic transfer switch (ATS) ensures seamless power during outages by switching to generator power automatically. This guide will explain its role and help you choose the best one for your needs. Key Takeaways An automatic transfer switch (ATS) is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted power by managing transitions between utility power and generator power during outages. There are three main types of ATS: open transition, closed transition, and bypass isolation, each suited for specific applications and operational needs. Selecting the appropriate ATS involves ensuring compatibility with generator voltages, considering the total amperage of circuits, and evaluating specific installation requirements for optimal performance. Understanding the Role of an Electric Generator Automatic Transfer Switch An automatic transfer switch (ATS) is a vital device that manages the switch between utility power and generator power. Here’s a straightforward breakdown: Purpose: When the main power source fails, the ATS activates, restoring power in seconds to ensure continuous electricity flow. This quick response is crucial for places like hospitals, data centers, and businesses that cannot afford downtime. Functionality: The ATS constantly monitors the primary power source for voltage and frequency. If it detects an issue, it swiftly switches from utility power to generator power. This ensures your backup power supply is always ready, maintaining operations smoothly. Importance: In hospitals, an ATS prevents critical medical equipment from shutting down during outages, safeguarding patient safety. For businesses, it avoids disruptions that could lead to revenue loss and reduced productivity. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right ATS for your specific […]
Read More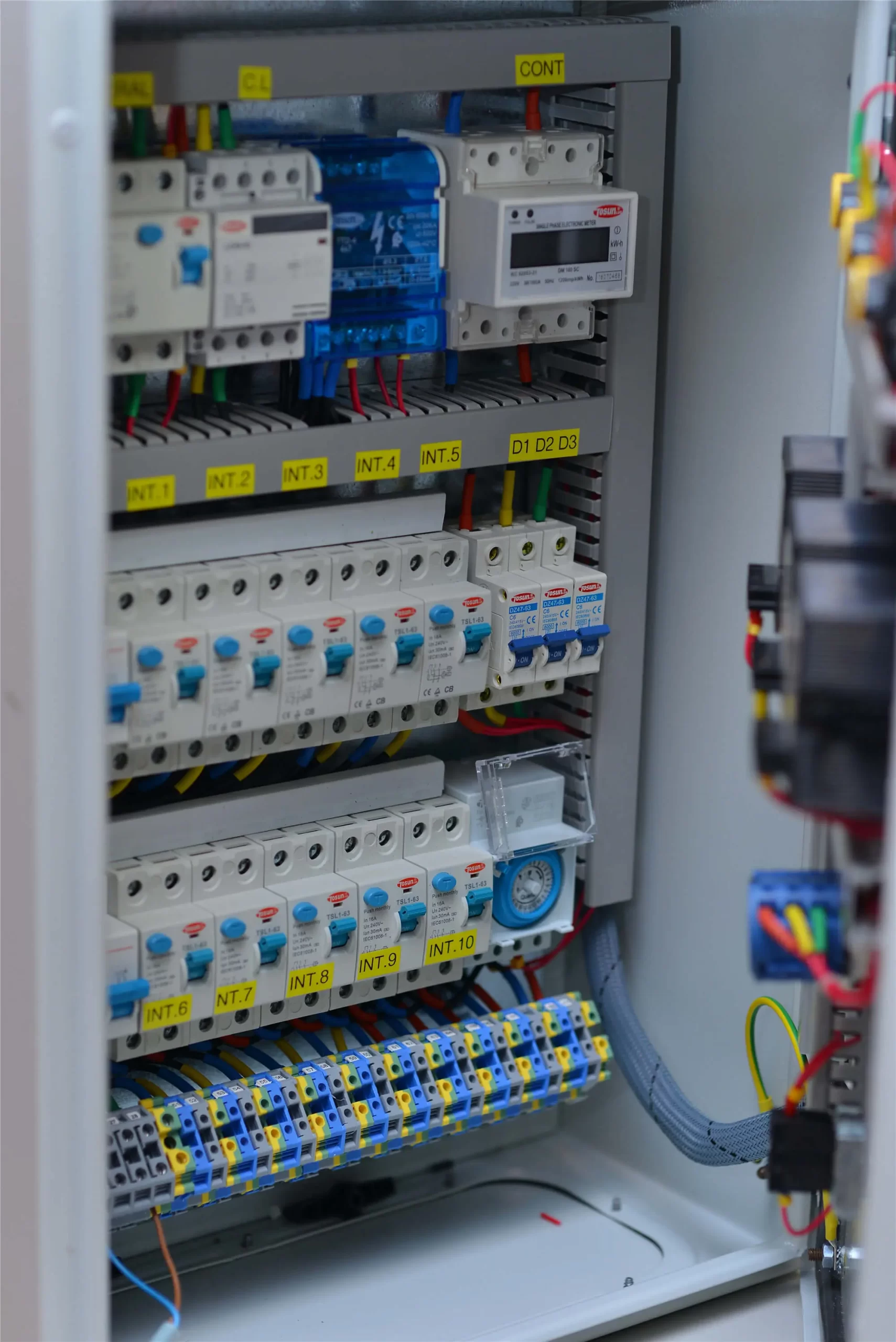
Did you know that low voltage circuit breakers can handle up to 1000 volts and currents ranging from 630 to 6300 amps, making them indispensable in both residential and commercial settings? In today’s world, where electrical safety is paramount, understanding the role of low voltage circuit breakers is crucial. This article delves into the advantages of using these circuit breakers, exploring their ability to prevent electrical faults, protect against electric shocks, and ensure the safety of electrical systems. We’ll also compare them with high voltage circuit breakers, highlight their versatile applications, and discuss their maintenance and installation benefits. Join us as we uncover the essential elements of low voltage circuit breakers and their impact on modern electrical systems. What is a Low Voltage Circuit Breaker? A low voltage circuit breaker is an electrical protection device designed to manage and interrupt electrical currents up to 1000 volts. It is commonly used in residential and commercial applications to prevent electrical faults, overloads, and short circuits. These breakers ensure safety by automatically disconnecting the electrical circuit when abnormal conditions are detected, such as excessive current flow or ground faults. Low voltage circuit breakers, including miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) and residual current circuit breakers (RCCBs), are essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of electrical systems. High Voltage Circuit Breaker Vs Low Voltage Circuit Breaker Feature High Voltage Circuit Breaker Low Voltage Circuit Breaker Voltage Range Above 1000 volts Up to 1000 volts Application Primarily used in industrial and utility sectors Commonly used in residential and commercial areas Current […]
Read More
Did you know that distribution boards are key to safely distributing electrical power in over 90% of homes and businesses, playing a crucial role in electrical distribution? These boards control electrical circuits, preventing faults and fires. In this article, we’ll explain what main distribution boards are, how they differ from sub distribution boards, and their role in safety. We’ll cover important parts like circuit breakers that stop overloads and short circuits. By the end, you’ll see how distribution boards keep electrical systems running smoothly. This easy-to-read guide is packed with data and expert tips to help you understand these important systems. The Main Function Of The Electrical Distribution Box The main function of a distribution box is to manage and distribute electrical power safely and efficiently throughout a building. Here’s a simple breakdown: Power Distribution: It receives power from the main supply or main power supply and distributes it to various circuits within a structure, ensuring that each part of the building gets the necessary electrical energy. Safety and Protection: The distribution box houses circuit breakers and other protective devices that prevent electrical faults and electrical hazards, such as overloads and short circuits, which can cause electrical fires. Control and Management: It allows for easy control over the electrical circuits or electrical circuits, making it convenient to perform maintenance or repairs by isolating specific areas without disrupting the entire electrical system. Centralized Monitoring: With all switches and meters in one place, it provides a centralized point for monitoring the electrical load or electrical loads and […]
Read More
Did you know that AC contactors are essential for controlling electrical devices like large motors and lighting installations? Understanding the differences between AC and DC contactors is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. This article dives into the key features, benefits, and applications of both AC and DC contactors, highlighting how they manage power supply, arc suppression, and heat generation. You’ll discover why AC contactors are preferred for fluctuating power and heavy motor currents, while DC contactors are ideal for steady current flows. Whether you’re an electrician, engineer, or curious learner, this comprehensive guide will equip you with valuable insights into these vital components of modern electrical systems. What Are AC Contactors? AC contactors are electrical devices used to control the flow of electricity in circuits. They operate using electromagnetic fields, which are created by a coil. The coil voltage can be powered by either an AC or DC supply. AC contactors consist of a coil, a moving iron core, and auxiliary contacts. Key Features: Coil Design: AC contactors have a ring-shaped coil made of iron with low resistance. This design helps generate a magnetic field that closes the power contacts. Magnetic Core: The magnetic core amplifies the magnetic flux produced by the coil. This magnetic force is essential for the contactor’s operation. Auxiliary Contacts: These allow a small amount of current to pass through and are usually connected to a control circuit. Applications: AC contactors are used in various applications, such as controlling electric motors, switching large lighting installations, and managing other electrical […]
Read MoreTel: +86-577-88671000
E-mail: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Address: Room No.1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center,Station Road, Wenzhou, China
WhatsApp us