Fused Disconnect Switch vs Circuit Breaker
21st Apr 2024
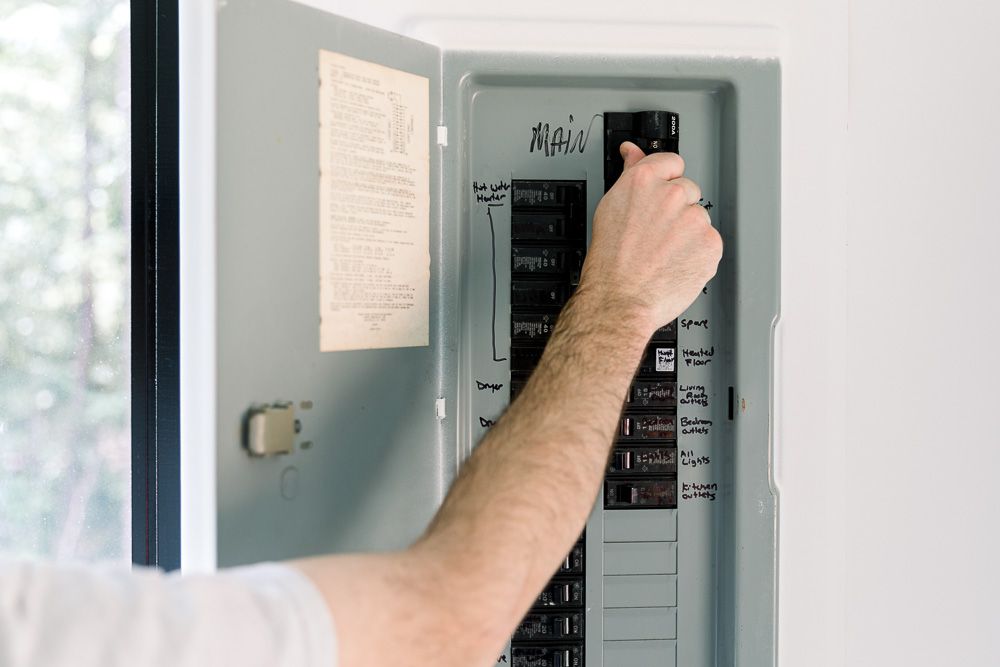
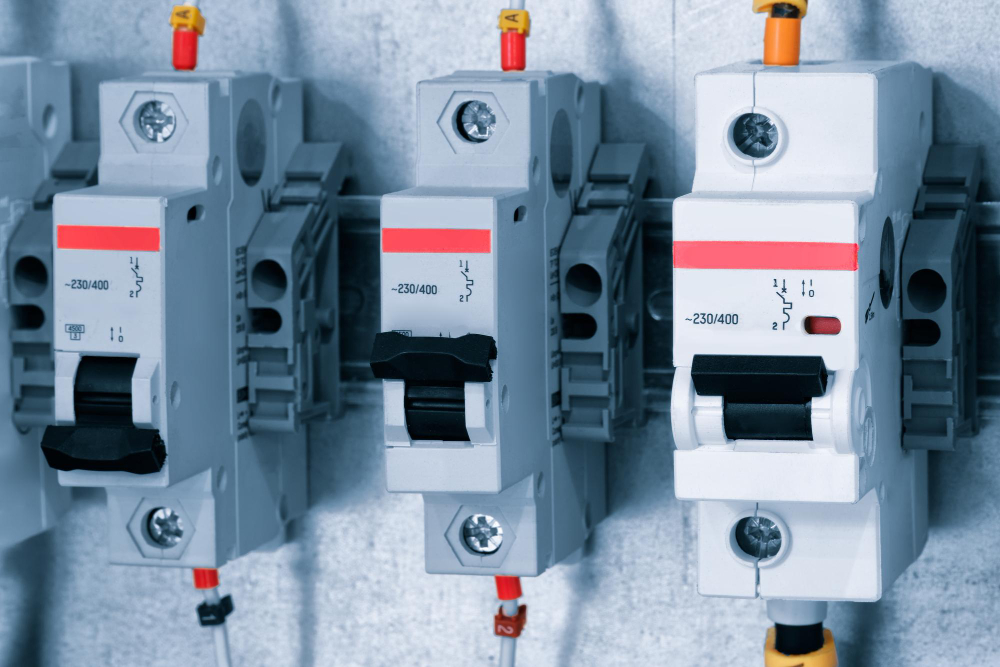
Overload protection comes in two main forms – fused disconnect switches and circuit breakers. Both open overloaded circuits, but have distinct ways of detecting issues and interrupting current flow. Fused switches rely on melted fuse elements to open circuits Circuit breakers have internal bimetal trip mechanisms Fuses allow very fast clearing in high-current situations Understanding a few key variances helps select the best choice. What is a Fused Disconnect Switch? A fused disconnect switch combines a manually-operated knife switch with one or more fixed current-rated fuses wired in series. During normal operation, contacts remain closed and allow unimpeded current flow to downstream equipment. No action occurs until an overload or short circuit event heats fuse elements beyond their capacity. At this point, the conductive metal literally melts and visually opens the circuit with certainty. Fused switches then require replacement of blown fuse elements before re-closing contacts. No resetting exists as with breakers – just replacement. Related Reading: What is a Fuse Switch Disconnector? What is a Circuit Breaker? A circuit breaker relies on an internal bimetal strip that predictably deforms under sustained overcurrent heat. The bimetal bending eventually releases a latch and trips open contacts to stop current flow. After cooling and manually toggling the handle off/on, the breaker can resume normal operation without replacement parts. This resettability contrasts with fused switches. Fused Disconnect Switch vs Circuit Breaker – Key Differences Here are a few key differences between the two variations: Clearing Severe Overloads Thanks to the very fast melting of calibrated fuse elements, fused […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά