How Does Digital Panel Meter Work?
14th Jul 2024
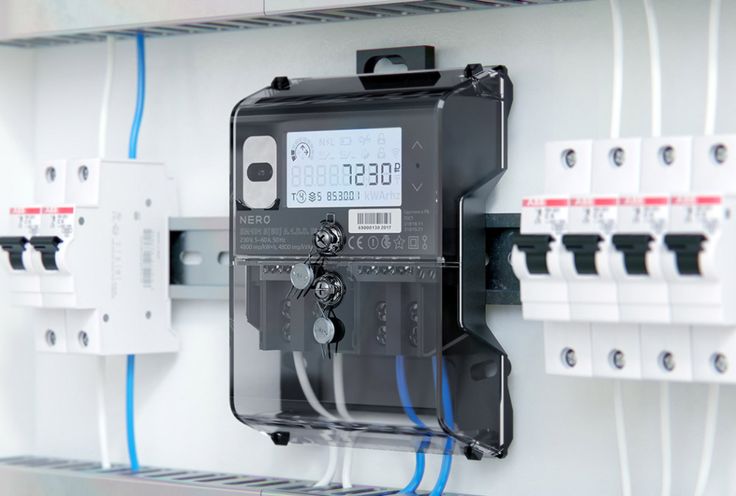
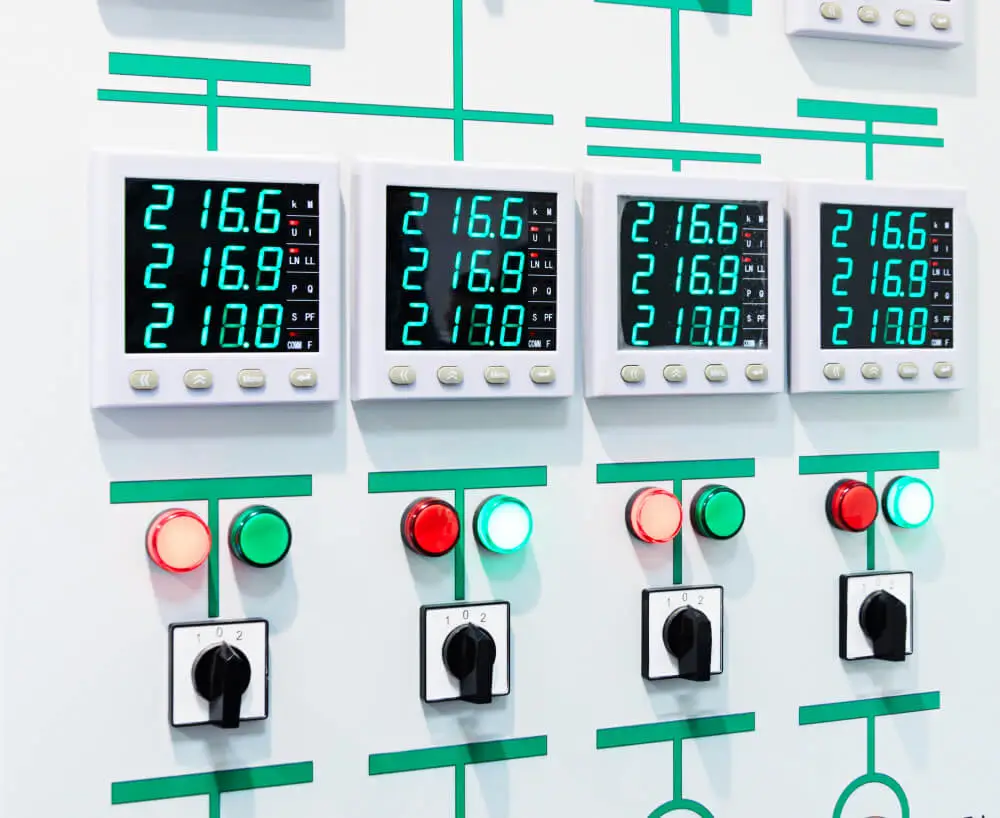
Let’s talk about digital panel meters, that little thing that plays a big role in monitoring electrical systems. What’s a digital panel meter? Digital panel meters are tools that measure and display various electrical parameters in a wide range of applications. They are versatile devices that provide accurate, real-time information which makes them indispensable in monitoring and controlling electrical systems. Digital Panel Meter: Working Principle How does a digital panel meter work? A digital panel meter works by converting analog electrical signals into digital values, which are then displayed on a screen for easy reading. It consists of several key components that make it work the way it does: input signal conditioning. analog-to-digital converter (ADC), microprocessor, and display which presents the measured value in a clear and readable format. The display can be an LCD, LED, or OLED screen, depending on the specific model. Measuring Techniques Digital panel meters use various measuring techniques to accurately capture different electrical parameters: Voltage Measurement Voltage is measured by comparing the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit. Digital panel meters use high-impedance input circuits to minimize loading effects and ensure accurate voltage readings. Current Measurement Current is typically measured using shunt resistors or current transformers (CTs). The voltage drop across the shunt resistor or the secondary winding of the CT is proportional to the current flowing through the circuit. The digital panel meter measures this voltage drop and calculates the corresponding current value. Power Measurement Digital panel meters can measure both active and reactive power in […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά