Do I Need A Fuse Between MPPT And Battery?
Table of Contents
ToggleDepending on the model of your MPPT, you may need a main fuse between the charge controller and the battery. The fuse size you choose will depend on the amps flowing to and from the charge controller.
Choosing the correct size fuse is crucial to ensure the safety and efficiency of your system. The size of the fuse is typically listed on the charge controller’s manual. For instance, if your MPPT draws 60 amps, you will want to connect the battery bank to starter circuit with a 60-amp fuse. You should also make sure the wires are long enough to connect to both components.
When using the MPPT charge controller, you must also use a PWM fuse. This fuse connects each panel to the charge controller. It should be located on the plus (+) side. You must make sure the fuse is placed between the MPPT charge controller and battery.
This fuse is important because it protects the charge controller from overcurrent and prevents the battery from reaching critical discharge. The fuse is also a safety measure to prevent damage to the battery, solar panel, and any electrical load.
If you want to know whether a fuse is required between MPPT and battery, continue reading this article.
What Is An MPPT Battery Fuse?
An MPPT battery fuse is an important piece of equipment when installing solar panels in your home. It can help protect your battery bank and inverter from excessive currents. A fuse can protect your system from a variety of situations and is essential to ensure that your solar panels are safe and functional.
A blown fuse can lead to malfunctioning of the power supply to your solar panel system, making it essential to regularly check and replace it if necessary.
Most charge controllers have a fuse built in. If your solar panels and MPPT battery charger have a fuse built in, yours likely has one as well. These protect the circuits from your batteries to your electric loads. This fuse is located on the positive battery line. It’s rated for 10 Amp.
The MPPT charge controller allows you to lower voltage and increase current as needed. When you use an MPPT battery fuse, make sure you use the right one. Fusing your battery post solar panel system improperly poses many risks. Always choose the correct wire size and type to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity.
The Importance of a Battery Fuse
A battery fuse is a critical component that protects the car’s electrical system from excessive current draw from the battery. Typically located in the positive terminal of the battery, the battery fuse is designed to prevent damage to the electrical system in case of a short circuit.
A blown battery fuse can cause a range of issues, including a dead car battery, malfunctioning accessories, and even a fire. Therefore, it’s essential to regularly check the battery fuse and replace it if necessary. Replacing a blown battery fuse is a relatively simple process, but it’s crucial to choose the correct fuse size and type to ensure the electrical system functions properly.
The battery fuse is an essential safety feature that helps prevent electrical shocks and fires. By ensuring that the battery fuse is in good condition and correctly rated, you can protect your car’s own supply, wiring and accessories from potential damage, keeping your vehicle safe and reliable.
Do I Need a Fuse Between MPPT and Battery?
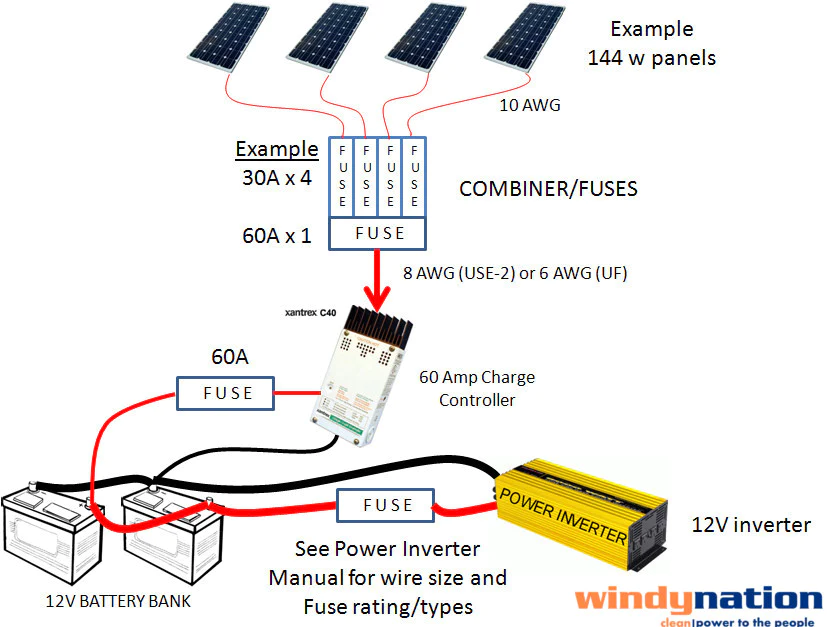
If you’re building a solar system, you need to determine the size of the fuse to connect your MPPT and battery. Most of the fuses are 50 amps, so you’ll need to choose one that matches the amp rating of the battery bank. In some cases, you might need a larger or smaller fuse depending on the battery bank and charge controller’s power ratings. Before installing a battery, however, you must turn off the solar panels.
Installing the correct fuse is essential to protect your car’s wiring from potential damage caused by excess current.
There are two types of fuses, thermal and magnetic. The former is a bi-metal strip that bends when heated, interrupting the current flow. The latter has an electromagnet embedded in it. When a large current flows through a circuit, the magnetic strip creates a magnetic force. The right fuse will protect your solar system and battery, ensuring that the MPPT’s performance is always stable.
To ensure that your MPPT is working properly, you need to install a fuse between the MPPT cable and the battery. In addition to batteries, you should also install a fuse between the PV string and the charge controller. In this case, the fuse should be at least 20 amps in size.
If you are using parallel PV strings, you can install a 30 amp fuse between the PV string and smaller wire for the charge controller, but if you want to connect a solar panel and a battery, you should use a 30 amp fuse. The MPPT must be able to regulate the current flowing into the battery bank. This is to protect the battery from overcharging. It will also reverse the flow of current during the night.
It is essential to choose a fuse that matches the charge controller amperage rating. If your MPPT charge controller has a 50 amp rating, you should choose a 50 amp fuse. But, if your battery is 50 amps, you should choose a fuse that matches that rating. This way, your batteries will never be damaged. You should also consider the amperage rating of the charge controller.
Using a circuit breaker over a fuse is a safer option. A circuit breaker protects against overheating and prevents damage from short circuits. A circuit breaker will automatically trip when a high current event is detected and reset when the current flows again.
Understanding Fuses and Their Role
Fuses are an essential component of a vehicle’s electrical system, designed to protect the car’s wiring and accessories from excessive current draw. Essentially, a fuse is a safety device that melts or breaks when the current flowing through it exceeds its amperage rating, thereby preventing damage to the electrical system.
Typically, fuses are located in a fuse box or fuse block, which is usually situated near the battery or in the engine compartment. The fuse protection box houses multiple fuses, each protecting a specific circuit or accessory, such as the starter, alternator, and fuel pump. This organization ensures that if one circuit experiences an overload, only the corresponding fuse will blow, leaving the rest of the system intact.
Fuses come in various sizes, including mega fuses, which are designed to handle high-current applications. Understanding how fuses work and their role in the electrical system is crucial for diagnosing and repairing electrical issues. By knowing which fuse protects which part of the system, you can quickly identify and address problems, ensuring your vehicle remains safe and functional.
Choosing the Correct Fuse
Choosing the correct fuse size and type is crucial to ensure the electrical system functions properly and safely. The correct fuse size depends on the electrical load of the circuit or accessory it’s protecting. A fuse that’s too small can blow frequently, causing inconvenience and potential damage to the system. Conversely, a fuse that’s too large can fail to protect the electrical system, leading to overheating and possible fires.
To determine the correct fuse size and type for each circuit or accessory, it’s essential to consult for example the owner’s manual or a wiring diagram. These resources provide the necessary information to select the appropriate fuse, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Using a fuse holder or fuse block can help organize and protect the fuses, making it easier to identify and replace blown fuses. By keeping all the wiring neat and accessible, you can quickly address any issues that arise, maintaining the integrity of your vehicle’s electrical system.
How to tell if a battery fuse is a blown fuse?
Use Multimeters to specify precise method: Set the multimeter at continuity settings. Touch probe to fuse point. When the multimeters are on and the continuity is visible, the fuse should be fine.
Regularly checking the fuse is crucial to ensure it is protecting all the wiring in your vehicle from potential short circuits.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be hazardous, and it’s essential to take safety precautions when diagnosing and repairing electrical issues. Always disconnect the positive ground negative terminal of the battery before starting work on the electrical system to prevent accidental shocks or short circuits.
Use protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when working with electrical systems. This gear helps protect you from potential injuries caused by electrical shocks or flying debris. Never touch electrical components or wiring with bare hands, as this can cause electrical shocks and further damage to the system.
If you’re unsure about any aspect of electrical system repair, consult a professional mechanic or the owner’s manual for guidance. Electrical systems can be complex, and it’s better to seek expert advice than to risk damaging your vehicle or injuring yourself. By following these safety considerations, you can work on your vehicle’s electrical system with confidence and care.
How much to replace a battery fuse box?
If you switch fuses on your own, one fuse could cost between $5 and $1.00 each.
Tel: +86-577-88671000
E-mail: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Address: Room No.1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center,Station Road, Wenzhou, China
REQUEST A QUOTE
WhatsApp us
 : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά



