How Is Electricity Distributed To Our Homes?
Table of Contents
ToggleElectricity powers our lives, from lighting homes to running appliances. But have you ever wondered how electricity reaches our home? The process involves several steps, each critical for ensuring safe and efficient delivery.
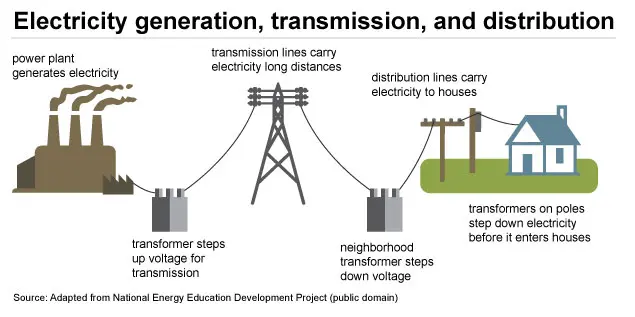
Step 1: Generating Electricity
The first step in delivering electricity to your home is generating it at power plants. These facilities use a mix of renewable and non-renewable energy sources to create electrical power.
- Renewable sources include wind, solar, and hydropower, offering cleaner and more sustainable energy.
- Non-renewable sources like coal and natural gas provide energy when renewable supplies are insufficient.
It means electricity generation involves converting energy into electrical power. For example:
- Thermal plants burn fossil fuels to produce steam, which drives turbines.
- Hydroelectric plants use flowing water to spin turbines directly.
- Solar panels generate electricity by converting sunlight into energy using photovoltaic cells.
The generated electricity is produced at high voltages, which reduces energy loss during transmission.
Step 2: Transmission – Sending Electricity Long Distances
Once electricity is produced, it enters the transmission network. These high-voltage lines carry electricity over long distances to local areas.
- Step-up transformers at power plants increase voltage to reduce energy loss.
- Transmission lines, supported by towers or running underground, act like highways for electricity.
This system ensures that electricity reaches regional substations efficiently and safely.
Step 3: Substations and Voltage Adjustment
At substations, electricity is prepared for distribution. Step-down transformers reduce the voltage to levels safe for homes and businesses.
It means that electricity, now at lower voltages, is ready to enter the local distribution network.
Step 4: Distribution to Neighborhoods
Electricity flows from substations into the distribution network, which includes:
- Overhead power lines that run along streets.
- Underground cables in areas where lines are buried.
- Local transformers that further lower voltage.
From here, electricity is routed to neighborhoods and connected to individual properties.
Step 5: How Electricity Reaches Our Homes
Electricity enters your home through a service drop connected to a meter box. The meter measures your consumption, ensuring accurate billing.
- Power divides into circuits.
- It flows through wires hidden behind walls.
- It powers outlets, switches, and all your appliances.
This process ensures that electricity safely and efficiently powers your home.
Embedded Generation: An Alternative
Another way electricity reaches homes is through embedded generation. Systems like rooftop solar panels generate electricity close to where it’s used. This approach reduces reliance on power plants and transmission lines while supporting cleaner energy use.
What Type of Electricity Is Used in Homes?
Homes rely on alternating current (AC) electricity. This standard, typically at 120V or 230V depending on the country, is ideal for safe and efficient power distribution.

Power your projects with reliable electrical solutions! Contact TOSUNlux for a personalized quote today.
Innovations in Home Electric Power Generation
More homeowners are exploring home electric power generation systems like solar panels and wind turbines. These systems allow individuals to generate electricity and store excess energy in batteries for later use. It means you can reduce reliance on the grid while supporting renewable energy efforts.
Understanding the Process
Every stage in the journey of electricity—from generation to distribution—ensures reliable and safe delivery. Whether through traditional power grids or newer embedded systems, electricity powers our lives efficiently.
FAQs
How does electricity reach our home?
Electricity travels from power plants through high-voltage transmission lines. It is stepped down at substations and distributed to homes through local networks.
What type of electricity is used in homes?
Homes use alternating current (AC) electricity, typically at 120V or 230V depending on the location.
Can I generate my own electricity?
Yes, you can install home electric power generation systems like solar panels or wind turbines.
Why is voltage adjusted during transmission?
Voltage is increased during transmission to reduce energy loss and decreased at substations to make it safe for home use.
What is the main electric power source for homes?
Most homes rely on a mix of renewable and non-renewable energy sources, with a growing shift toward solar and wind.
By understanding the journey of electricity, you can appreciate the infrastructure that brings power to your home. Each stage ensures the electricity you use is safe, efficient, and reliable.
Tel: +86-577-88671000
E-mail: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Address: Room No.1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center,Station Road, Wenzhou, China
REQUEST A QUOTE
WhatsApp us
 : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά


