Digital Panel Meters vs Analog Panel Meters: How to Choose
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen it comes to selecting panel meters for measuring and displaying electrical parameters, the choice often comes down to digital panel meters and analog panel meters.
So which should you choose between the two?
Digital and Analog Panel Meters
An analog panel meter, also known as an analog meter, is a traditional type of measuring instrument that uses a moving pointer or needle to indicate the value of the measured parameter on a graduated scale. The movement of the pointer is typically driven by an electromechanical mechanism, such as a moving coil or an iron vane.
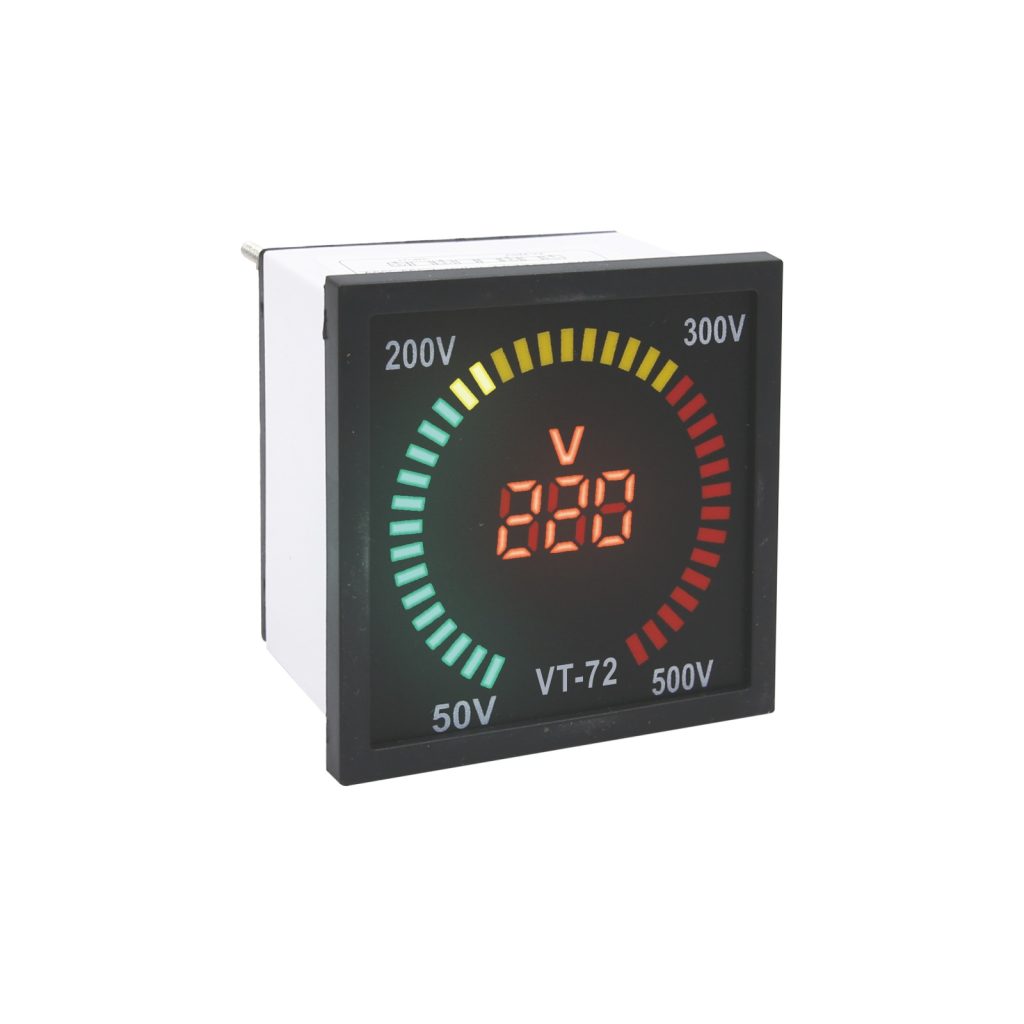
On the other hand, a digital panel meter, or digital meter, is a modern measuring device that displays the measured value in a digital format using a numerical display, such as an LCD or LED screen. Digital panel meters rely on electronic circuits and microprocessors to process and display the measured data.
Key Differences between Analog Meter vs Digital Meter
Display
The most obvious difference between analog and digital panel meters is the way they display the measured value. Analog meters use a moving pointer and a graduated scale, while digital meters provide a precise numerical readout.
Accuracy
Digital panel meters generally offer higher accuracy compared to analog meters. Digital meters can provide readings with a resolution of up to several decimal places, while analog meters are limited by the resolution of the graduated scale and the user’s ability to interpret the pointer position.
Reading Ease
Digital panel meters provide an unambiguous reading, eliminating the need for interpolation or parallax error correction. Analog meters, on the other hand, may require the user to estimate values between scale markings and account for parallax errors when viewing the pointer position from an angle.
Functionality
Digital panel meters often offer additional features and functionalities beyond basic measurements, such as data logging, alarm setpoints, communication interfaces, and programmable settings. Analog meters are typically limited to displaying the instantaneous measured value.
Durability
Analog panel meters, with their electromechanical components, are generally more susceptible to wear and tear over time. Digital panel meters, being solid-state devices, tend to have a longer lifespan and are more resistant to vibration and shock.
Cost
Analog panel meters are often less expensive than their digital counterparts, making them a cost-effective choice for basic measurement applications. However, the price difference has narrowed in recent years as digital technology has become more affordable.
Pros and Cons of Analog and Digital Panel Meters
Analog Digital Panel Meter
| PROS | CONS |
| Lower upfront cost | Lower accuracy compared to digital meters |
| Simple and intuitive to read | Limited resolution and functionality |
| No power supply is required (for some models) | Susceptible to parallax errors and interpolation inaccuracies |
| Suitable for basic measurement applications | Prone to wear and tear |
Digital Panel Meters
| PROS | CONS |
| High accuracy and resolution | Higher upfront cost |
| Clear and precise numerical display | Requires a power supply |
| Advanced features and functionalities | Potential for digital display glitches or failures |
| Durable and resistant to vibration and shock | Learning curve for users unfamiliar with digital interfaces |
| Easy integration with automation systems |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Analog and Digital Panel Meters
When deciding between an analog meter vs digital meter, consider the following factors:
Application Requirements
Evaluate the specific needs of your application, including the required accuracy, resolution, and functionality. Applications demanding high precision and advanced features may benefit from digital panel meters, while basic measurement tasks can often be accomplished with analog meters.
Budget
Consider the available budget for your panel meter investment. While analog meters are generally less expensive upfront, the long-term benefits of digital meters, such as increased accuracy and functionality, may justify the additional cost.
User Preferences
Take into account the preferences and familiarity of the users who will be interacting with the panel meters. Some users may find analog meters more intuitive and easier to read at a glance, while others may appreciate the precise readouts and advanced features of digital meters.
Integration with Existing Systems
If the panel meters need to be integrated with existing automation or data acquisition systems, consider the compatibility and communication capabilities of the chosen meter type. Digital panel meters often offer a wider range of communication interfaces and protocols compared to analog meters.
Environmental Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions in which the panel meters will be operating. Harsh environments with vibration, shock, or extreme temperatures may favor the durability and stability of digital panel meters over analog meters with moving parts.
Maintenance and Calibration
Evaluate the long-term maintenance and calibration requirements of the panel meters. Digital meters generally require less frequent calibration and maintenance compared to analog meters, which may need periodic adjustments and replacement of mechanical components.
Tosunlux: Your Trusted Partner for Panel Meter Solutions
At Tosunlux, we understand the importance of selecting the right panel meter for your specific application. As a leading provider of panel meters, we offer a comprehensive range of solutions to meet your measurement needs.
Experience the Tosunlux difference and unlock the full potential of your electrical measurement capabilities. Contact us today to learn more about our panel meter offerings and how we can help you achieve your objectives. Trust Tosunlux to be your partner in precision and performance.
Contact us today to learn more!
Tel: +86-577-88671000
E-mail: ceo@tosun.com
Skype: tosunelectric
Wechat: +86-139 6881 9286
WhatsApp: +86-139 0587 7291
Address: Room No.1001 Wenzhou Fortune Center,Station Road, Wenzhou, China
REQUEST A QUOTE
WhatsApp us
 : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά