The Advantages of Thermal Relay Protection
04th Apr 2025
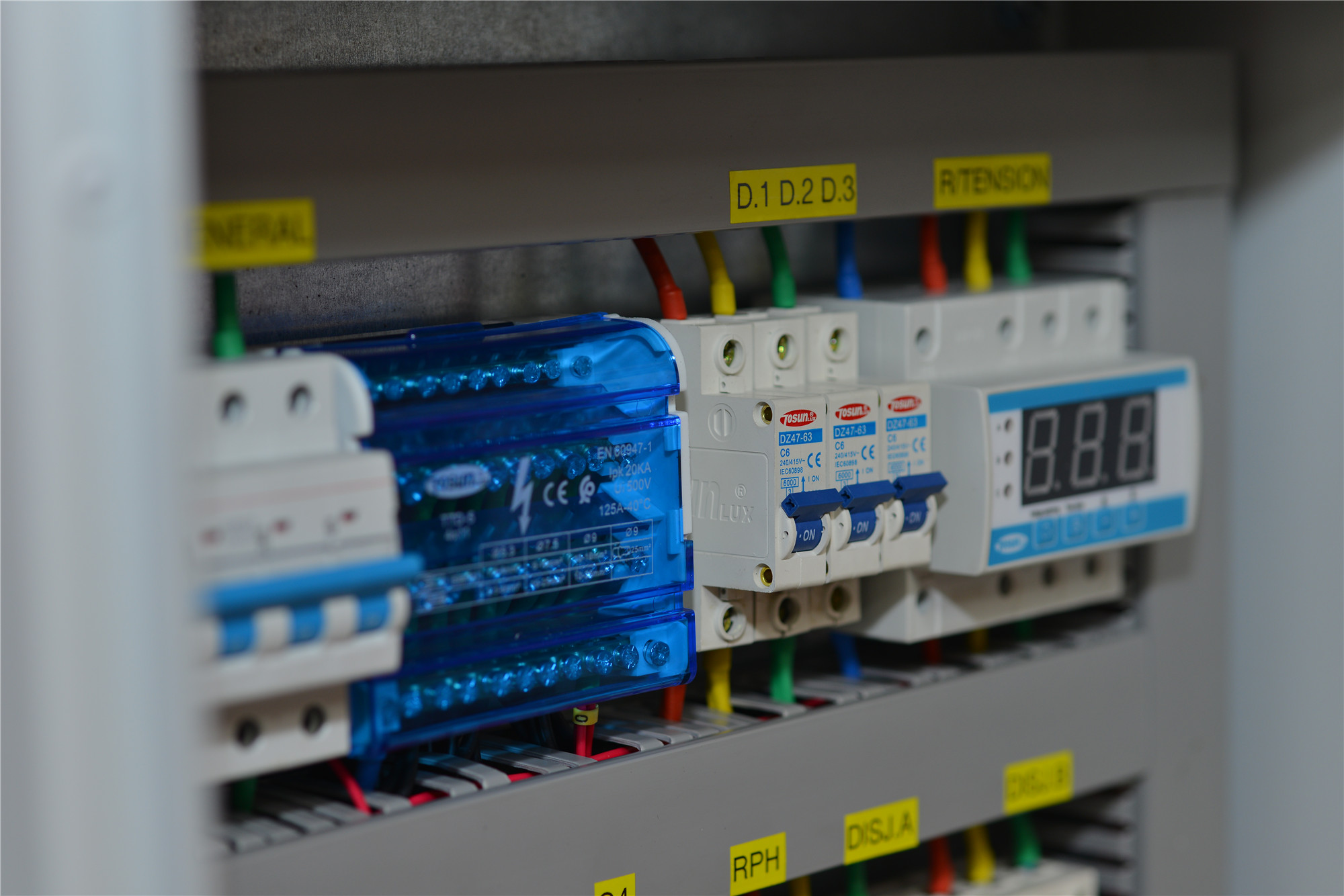
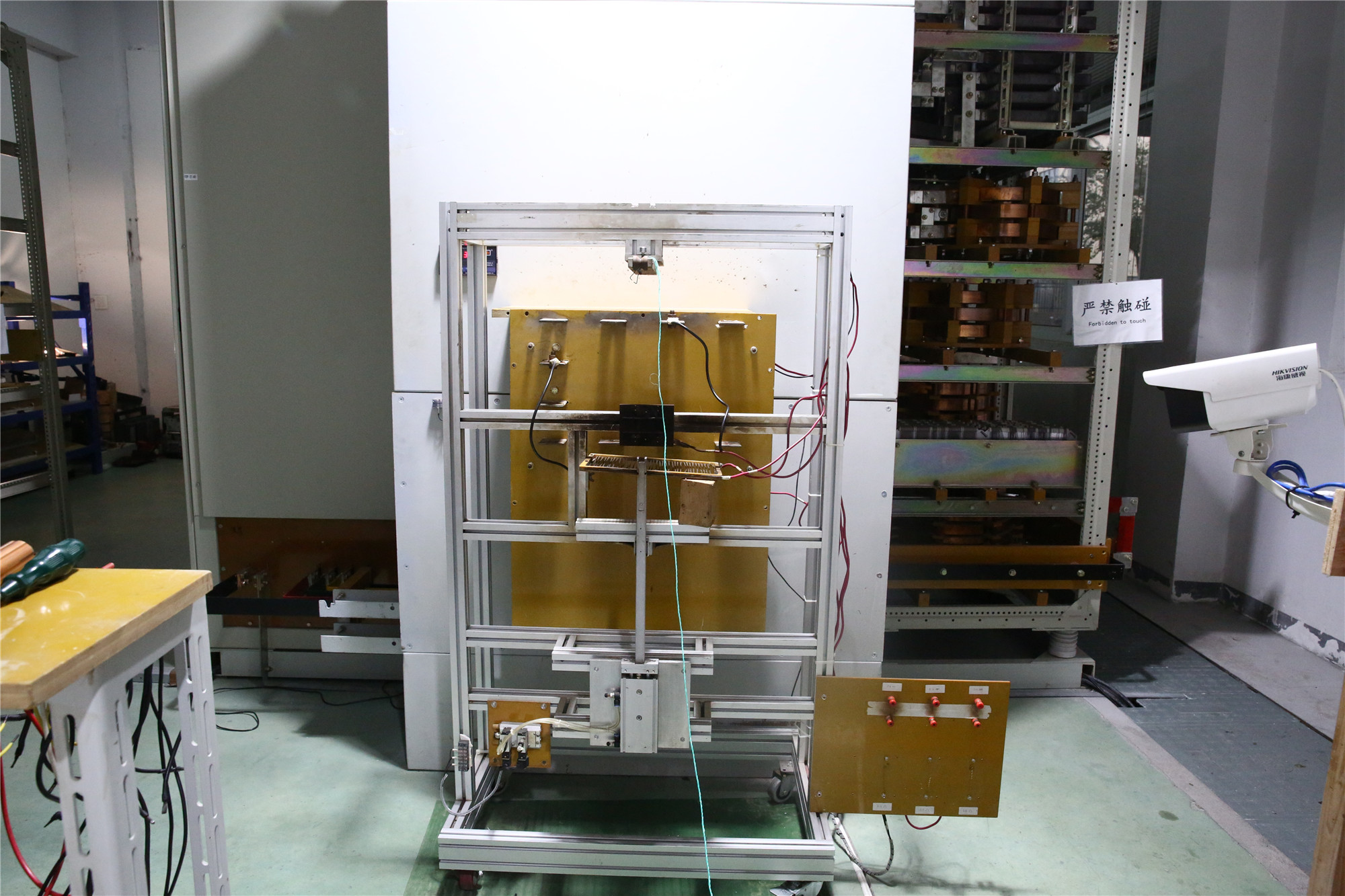
Thermal relay protection is essential for safeguarding electrical circuits from overheating and damage. It works by monitoring the heat in circuits and interrupting the power supply if temperatures get too high, preventing failures and extending equipment life. In this article, we will explore what thermal relay protection is, how it works, and its benefits and drawbacks. What is Thermal Relay Protection? Thermal relay protection prevents overheating and short circuits in manual control electrical circuits. A thermal overload relay monitors heat within an electrical circuit. If a motor draws excessive current, leading to potential damage, the relay trips to interrupt the circuit and prevent further harm. Thermal overload relays protect motors from electrical overloads by detecting heat during operation. If the temperature exceeds a safe threshold, the thermal overload relay responds, and the relay trips to cut the power supply, preventing motor failure and extending equipment life. Understanding how thermal overload relay work is essential for effective motor protection. For instance, the Chint Thermal Overload Relay prevents fires and electrical problems while protecting cable systems during excessive current situations. These relays are crucial in preventing permanent damage from overheating, making them indispensable for motor protection, system reliability, and as an overload protection device. Auto Reset vs Manual Reset on Thermal Overload Relays Feature Auto-Reset Thermal Overload Relays Manual Reset Thermal Overload Relays Operation Automatically restarts the motor after cooling. Requires external action to restart the motor after a trip. Safety May pose risks due to unintended motor restarts. Safer as it ensures investigation and resolution of […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά